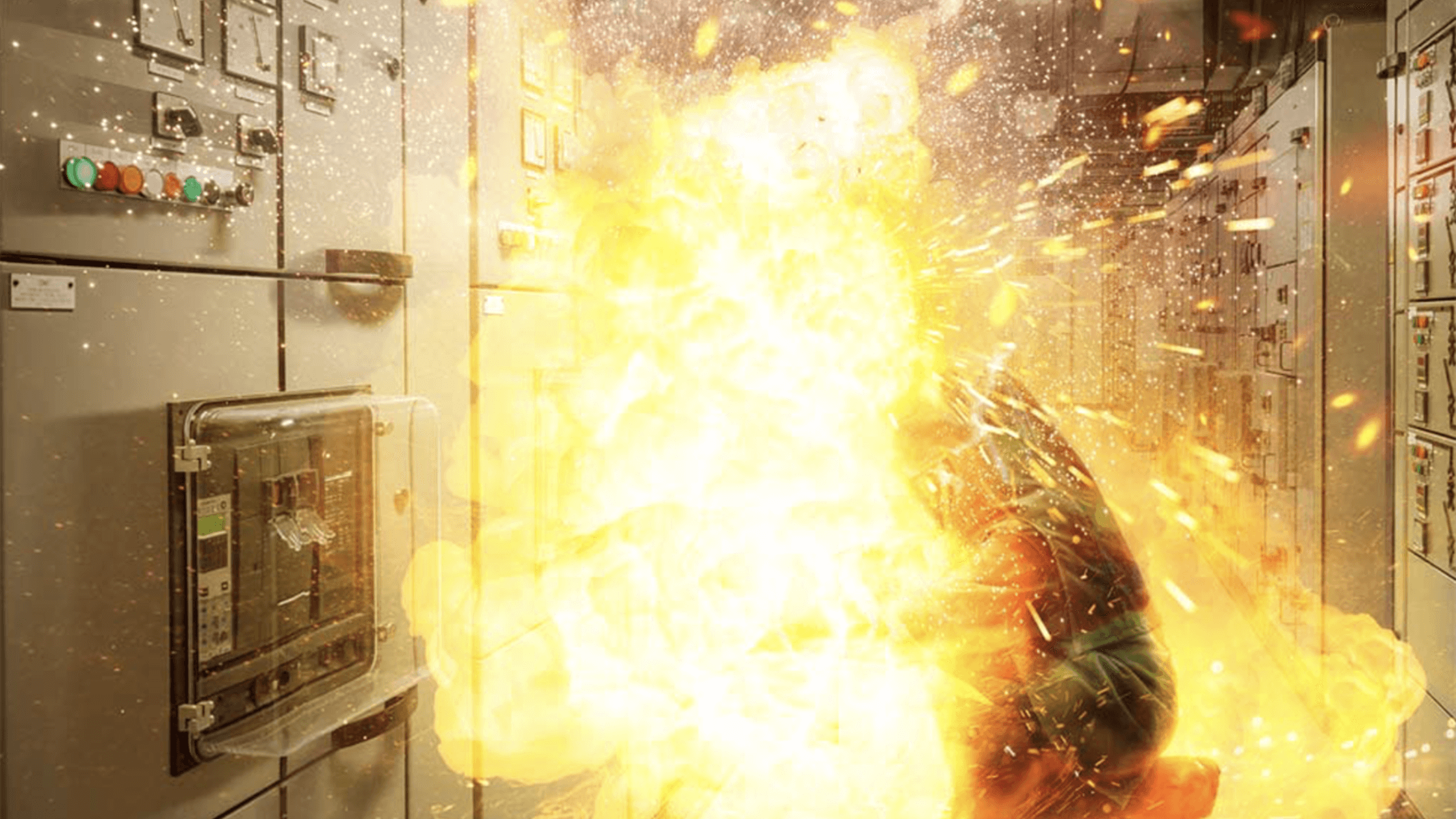
Electricians, engineers, and construction workers face a serious but often overlooked danger—arc flashes. These sudden electrical explosions can reach temperatures hotter than the surface of the sun, causing severe burns, injuries, and even fatalities in an instant. Understanding what causes arc flashes and how to prevent them is essential for keeping job sites safe and protecting workers from life-threatening hazards.
Quick look
- Arc flashes are extreme electrical discharges that can cause severe burns, explosions, and life-threatening injuries in construction and engineering.
- Key causes include equipment failure, human error, and poor maintenance, making regular inspections and safety protocols essential.
- Preventive measures such as safety training, PPE, and clear labeling help reduce risks and protect workers from dangerous arc flash incidents.
- A strong electrical safety program and risk assessment procedures ensure compliance with industry standards and create safer job sites.
What are arc flashes?
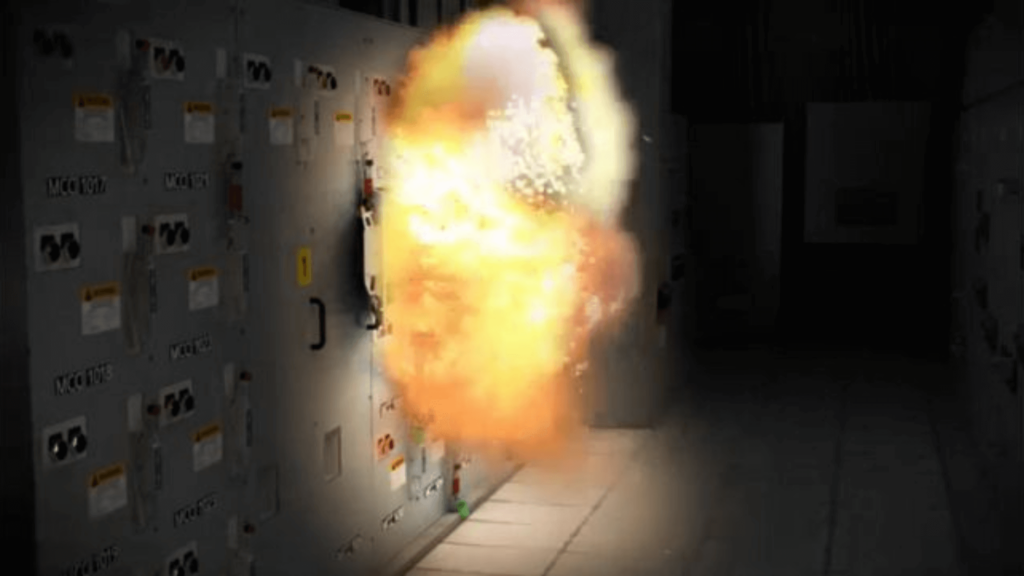

An arc flash occurs when an electrical current leaves its intended path and travels through the air to another conductor or the ground. This uncontrolled discharge generates intense heat, bright light, and explosive force in a fraction of a second. This rapid release of energy produces extreme heat, intense light, and a powerful blast, all within milliseconds. Even a small arc flash can cause severe burns, equipment damage, and job site disruptions.
Arc flash vs. arc blast
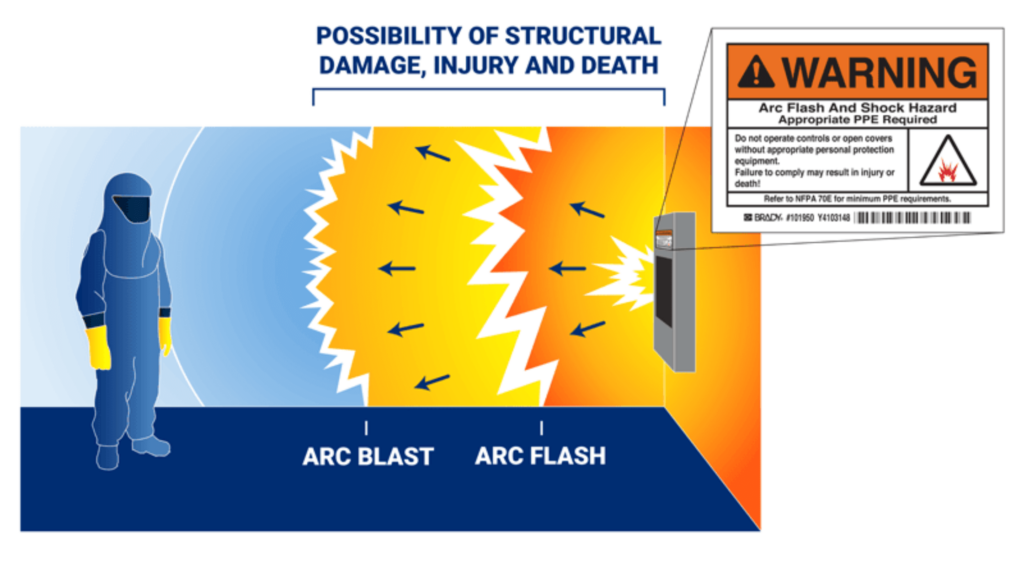
While often used interchangeably, arc flashes and arc blasts are different.
- Arc flash: A high-temperature discharge that creates intense heat and bright light, leading to burns, fires, and potential vision damage.
- Arc blast: The explosion that follows an arc flash, generating pressure waves strong enough to knock workers off their feet, hurl molten metal, and rupture eardrums.
What causes an arc flash?
Arc flashes don’t happen randomly—they are triggered by specific conditions that allow electricity to escape its intended path. These incidents can lead to devastating injuries and costly damage, whether due to equipment failure, environmental factors, or human error.
- Equipment failure or deterioration: Electrical components wear down over time, increasing the risk of unexpected faults. Aging wires, circuit breakers, and switchgear can become weak points for an arc flash.
- Human error: Working on energized equipment without proper safety protocols significantly increases the risk. Accidental contact with live components or incorrect tools can trigger an arc flash instantly.
- Dust, moisture, or contaminants: Dirt, dust, and moisture can create conductive paths inside electrical panels, leading to dangerous short circuits. In some cases, these contaminants can also corrode connections, further increasing the risk.
- Loose or corroded connections: Poorly secured electrical connections can create resistance and overheating, which may lead to an arc flash. Regular inspections help identify and fix these weak points before they become hazardous.
- Poorly maintained electrical systems: Neglecting routine maintenance increases the likelihood of faults that could spark an arc flash. Preventive care, such as infrared scanning and thermographic inspections, can detect hidden issues before they lead to disaster.
Arc flash dangers and risks
The consequences of an arc flash go beyond a brief electrical discharge—they can be life-altering. The intense heat, explosive pressure, and flying debris create a dangerous environment where severe injuries or fatalities can happen in an instant. Understanding these risks is crucial for enforcing proper safety measures on job sites.
Burns
Arc flashes can reach up to 35,000°F (19,400°C), instantly vaporizing metals and causing severe burns. In a fraction of a second, exposed skin can suffer third-degree burns, while synthetic clothing may ignite, causing further injuries. Even workers several feet away from the arc flash can experience severe burns due to radiant heat.
Blast injuries
An arc blast can create a pressure wave exceeding 2,000 lbs/sq ft—enough force to rupture eardrums, cause concussions, and throw workers several feet. The impact of the blast can knock workers into nearby equipment, leading to additional trauma.
Flying debris and shrapnel
Molten metal fragments and shattered equipment components become dangerous projectiles during an arc flash. Workers caught in the blast zone can suffer deep lacerations, impalement injuries, or even blindness if struck by flying debris.
Toxic fumes
The intense heat of an arc flash vaporizes metals, insulation materials, and coatings, releasing harmful gases into the air. Inhalation of these toxic fumes can cause lung irritation, respiratory issues, or long-term health complications.
How to prevent arc flashes and stay safe
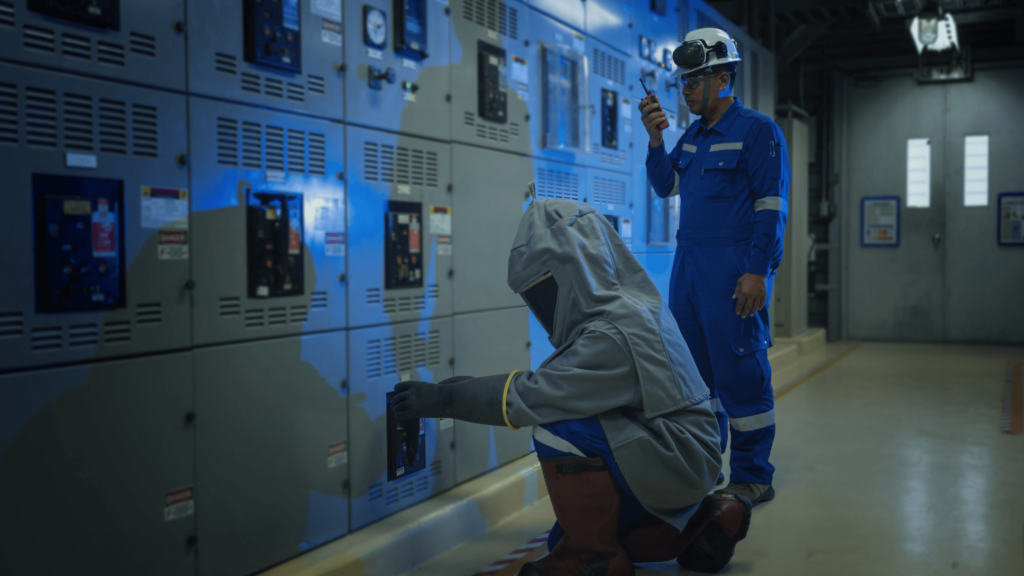

Arc flashes are dangerous, but they’re also preventable. A proactive approach to electrical safety can significantly reduce the risk of incidents. From establishing clear procedures to ensuring workers are properly trained, taking the proper precautions can help protect both workers and equipment.
1. Implement an electrical safety program
A structured electrical safety program is the foundation of arc flash prevention. It establishes clear guidelines for working with electrical systems and helps workers, supervisors, and contractors follow best practices. Key components include:
- Lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures: Enforcing strict protocols ensures that electrical equipment is properly de-energized before maintenance or repairs. This prevents unexpected re-energization, which is a common cause of arc flashes.
- Arc flash safety training: Workers must be trained in hazard recognition, proper equipment use, and emergency response. Understanding how to work safely with or around electrical panels and high-voltage systems can prevent accidents before they happen.
2. Develop a risk assessment procedure
A proactive approach to risk assessment helps identify potential arc flash hazards before they become a threat. Evaluating electrical systems and determining their danger levels allows teams to implement targeted safety measures that reduce risk.
- Identify high-risk electrical systems: Regular hazard assessments should focus on high-voltage areas, aging equipment, and frequently serviced panels, as these are more likely to experience arc flash incidents.
- Arc flash incident energy calculations: Conducting incident energy calculations helps determine the severity of a potential arc flash, ensuring workers wear the appropriate PPE and follow the proper safety procedures.
3. Use proper PPE
Even with strong safety protocols, arc flashes remain a serious hazard. Wearing the correct PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) is critical for reducing the severity of injuries if an incident occurs.
- Arc-rated flame-resistant clothing: Standard workwear won’t protect against extreme heat. Workers should wear arc-rated flame-resistant (FR) clothing to prevent ignition and melting.
- Gloves, face shields, and insulating tools: Arc-rated gloves and face shields help prevent burns and eye injuries, while insulated tools add an extra layer of protection against electrical contact.
- NFPA 70E compliance: PPE should meet NFPA 70E standards, ensuring adequate protection against arc flash hazards in different work environments.
4. Proper labeling of equipment
Clear, accurate electrical equipment labeling helps workers identify hazards before interacting with potentially dangerous systems. Proper signage ensures that workers understand voltage levels, PPE requirements, and safety precautions at a glance.
- Mark electrical panels and high-voltage areas: Arc flash warning labels should be placed on all electrical panels, switchgear, transformers, and high-voltage equipment to alert workers to potential risks.
- Ensure labels include key safety information: Labels should display voltage levels, required PPE, arc flash boundaries, and hazard classifications, helping workers determine the correct safety protocols before performing maintenance.
Bottom line
Arc flashes are one of the most dangerous electrical hazards in the AEC industry but are also highly preventable. Understanding the causes, risks, and safety measures is key to protecting workers from severe burns, blast injuries, and long-term health complications.
Stay ahead of industry safety updates, best practices, and expert insights. Subscribe to our newsletter today to get the latest news delivered straight to your inbox.


