The construction industry has seen incredible technological advancements recently, but Building Information Modeling (BIM) stands out as a transformative innovation. BIM offers a smarter, more collaborative way of managing construction projects, helping stakeholders plan, design, and execute with greater accuracy. But what exactly is BIM, and why are so many companies adopting it?
The basics of BIM (Building Information Modeling)
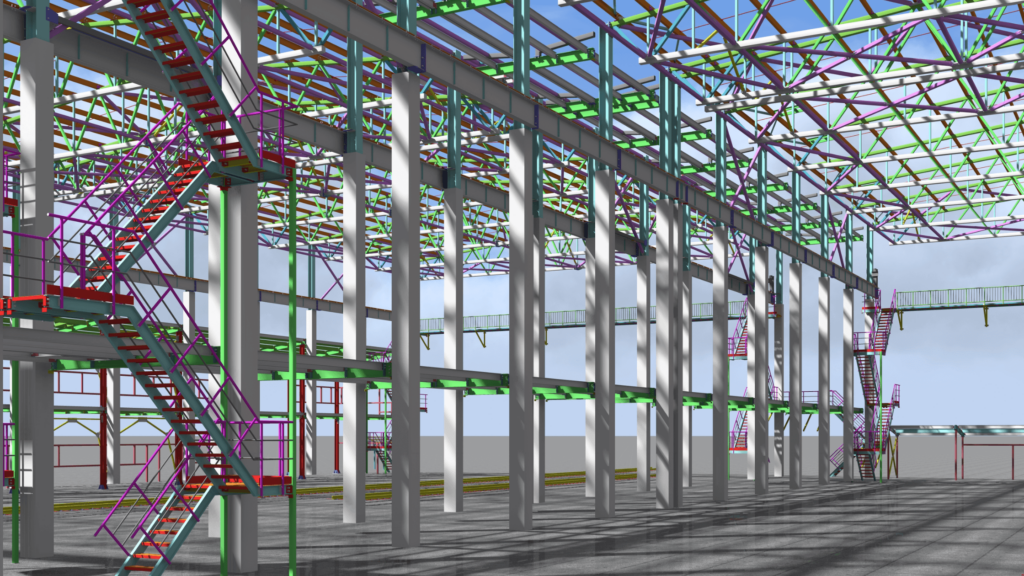
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital process that creates a detailed representation of a building’s physical and functional characteristics. More than just a 3D model, BIM acts as a shared knowledge resource for all project stakeholders, enabling better decision-making throughout a building’s entire lifecycle—from initial concept to demolition.
Subsets of BIM
BIM’s power lies in its ability to organize and present information in dimensions beyond just 3D. These subsets offer distinct ways to manage and optimize construction projects:
- 3D (Object Model): Focuses on visualizing the physical structure, allowing for precise modeling and design.
- 4D (Time): Incorporates scheduling data to visualize the construction timeline, ensuring better sequencing and resource allocation.
- 5D (Cost): Adds financial data, enabling cost estimation and budgeting directly within the model.
- 6D (Operation): Helps with facility management by centralizing operational data for easier maintenance and upgrades.
- 7D (Sustainability): Supports environmental goals by integrating energy analysis and sustainability metrics.
- 8D (Safety): Enhances safety planning by identifying potential risks and mitigating hazards before construction begins.
Each of these dimensions offers a unique perspective on the project, allowing teams to tackle challenges with a more comprehensive and streamlined approach.
Applications of BIM
Modeling
BIM begins with creating a detailed 3D model of the building, incorporating architectural, structural, and mechanical elements. This model serves as the foundation for team collaboration, offering a shared visual reference. Features like clash detection ensure that different systems (like plumbing and electrical) don’t interfere with each other during construction. By resolving these conflicts digitally, teams save time and reduce costly on-site adjustments.
Workflow
BIM streamlines workflows by acting as a centralized hub for all project data. Stakeholders, including architects, engineers, and contractors, can access and update information in real-time. This eliminates the need for multiple versions of documents and ensures consistency across the board. For example, if an engineer updates the HVAC system design, the changes are immediately reflected in the model, allowing other teams to adapt their plans accordingly.
Construction
During construction, BIM acts as a guide for workers on-site. The model provides detailed instructions for assembly, material usage, and sequencing. Integrating 4D (time) data allows project managers to visualize construction schedules and identify potential delays. Additionally, tools like augmented reality (AR) can overlay the BIM model onto the physical site, helping workers align their tasks with the digital design.
Handover
BIM’s utility doesn’t end when construction is complete. The detailed digital model is handed over to facility managers, providing them with a comprehensive database of the building’s components and systems. This includes information about warranties, maintenance schedules, and operational guidelines, making managing the building throughout its lifecycle easier. Having all this data in one place makes future renovations and repairs more efficient and cost-effective.
Risk management
By integrating safety planning into BIM, teams can identify potential hazards and develop strategies to mitigate risks before they occur. For example, the model can simulate site conditions to pinpoint areas prone to accidents or unsafe practices.
Energy analysis and sustainability
With BIM’s sustainability features, teams can evaluate a building’s energy consumption and environmental impact during the design phase. This helps optimize insulation, ventilation, and energy systems for a more eco-friendly structure.
10 ways BIM is impacting the construction industry
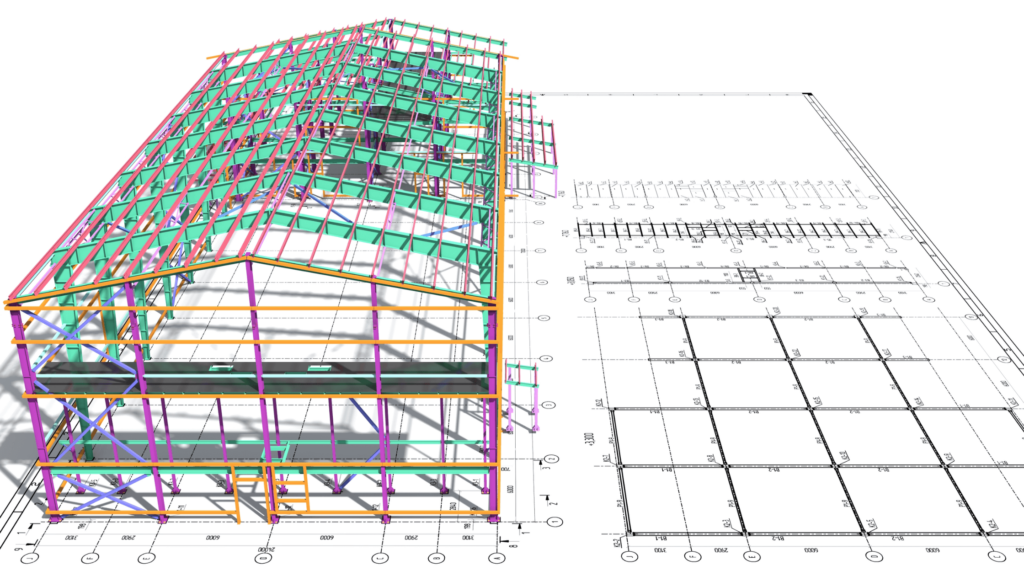
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has significantly transformed the construction industry, offering numerous advantages that enhance project outcomes. Here are the ten biggest benefits of using BIM in your project:
- Enhanced collaboration and communication: BIM provides a centralized platform where all stakeholders—architects, engineers, contractors, and owners—can access and update project information in real-time. This shared environment fosters better collaboration and reduces misunderstandings.
- Improved cost estimation and budget management: By integrating cost data into the BIM model (5D BIM), teams can generate accurate cost estimates and monitor budgets throughout the project lifecycle. This transparency helps in making informed financial decisions and controlling expenses.
- Reduced rework and errors: BIM’s clash detection capabilities identify conflicts between different building systems early in the design phase, allowing teams to address issues before construction begins. This proactive approach minimizes costly rework and delays.
- Enhanced scheduling and sequencing: Incorporating time-related data (4D BIM) enables project managers to visualize construction sequences and develop efficient schedules. This visualization aids in resource allocation and helps prevent scheduling conflicts.
- Improved safety planning: BIM allows for the simulation of construction processes, helping to identify potential hazards and develop safety plans accordingly. This foresight contributes to safer construction sites and reduces the risk of accidents.
- Better facility management and maintenance: Post-construction, BIM is a comprehensive repository of building information, aiding facility managers in maintenance, renovations, and operations. Access to detailed data about building components streamlines maintenance activities.
- Enhanced sustainability and energy efficiency: BIM facilitates the analysis of energy performance and environmental impact during the design phase, allowing for the selection of sustainable materials and systems. This leads to more energy-efficient buildings with reduced environmental footprints.
- Increased prefabrication and modular construction: Detailed BIM models support the design and fabrication of building components off-site, promoting prefabrication and modular construction methods. This approach enhances construction speed and quality while reducing waste.
- Improved quality control: BIM enables thorough documentation and visualization of design elements, ensuring that construction meets specified standards and quality benchmarks. This meticulous attention to detail results in higher-quality outcomes.
- Enhanced client satisfaction: BIM helps clients better understand the project scope and progress by providing clear visualizations and accurate information. This transparency fosters trust and leads to higher levels of client satisfaction.
Incorporating BIM into construction projects offers these tangible benefits, leading to more efficient processes and successful project outcomes.
The challenges of BIM
While BIM has transformed the construction industry, its complexity remains a significant hurdle for many contractors. Unlike project owners who see long-term value in BIM’s 3D modeling and lifecycle management capabilities, many contractors struggle with the platform’s steep learning curve. The usability of BIM models often depends on expert handling, as inconsistent data and poor-quality models can render the technology difficult to navigate. For teams without specialized training, extracting relevant information from a BIM model feels more like an obstacle than a solution.
This complexity also introduces added risks. Contractors who make changes within the model often take on unintended design liability, an issue many are unprepared to handle. Without proper support or clear protocols, BIM’s potential remains frustratingly out of reach for many contractors.
Bottom line
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is reshaping the construction industry, offering a smarter, more collaborative approach to designing, building, and managing structures. Its ability to streamline workflows, reduce errors, and improve project outcomes has the potential to make it a valuable tool for modern construction teams. However, like any transformative technology, BIM has challenges, particularly for those new to its complexities. Proper training, clear protocols, and professional support are essential to unlocking its full potential.
By investing in the right resources and strategies, companies can stay ahead of the curve and deliver more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable projects.
Interested in staying ahead of the curve about the latest innovations in construction technology? Subscribe to our newsletter for insights, tips, and updates on integrating BIM and other tools into your projects.


6 comments