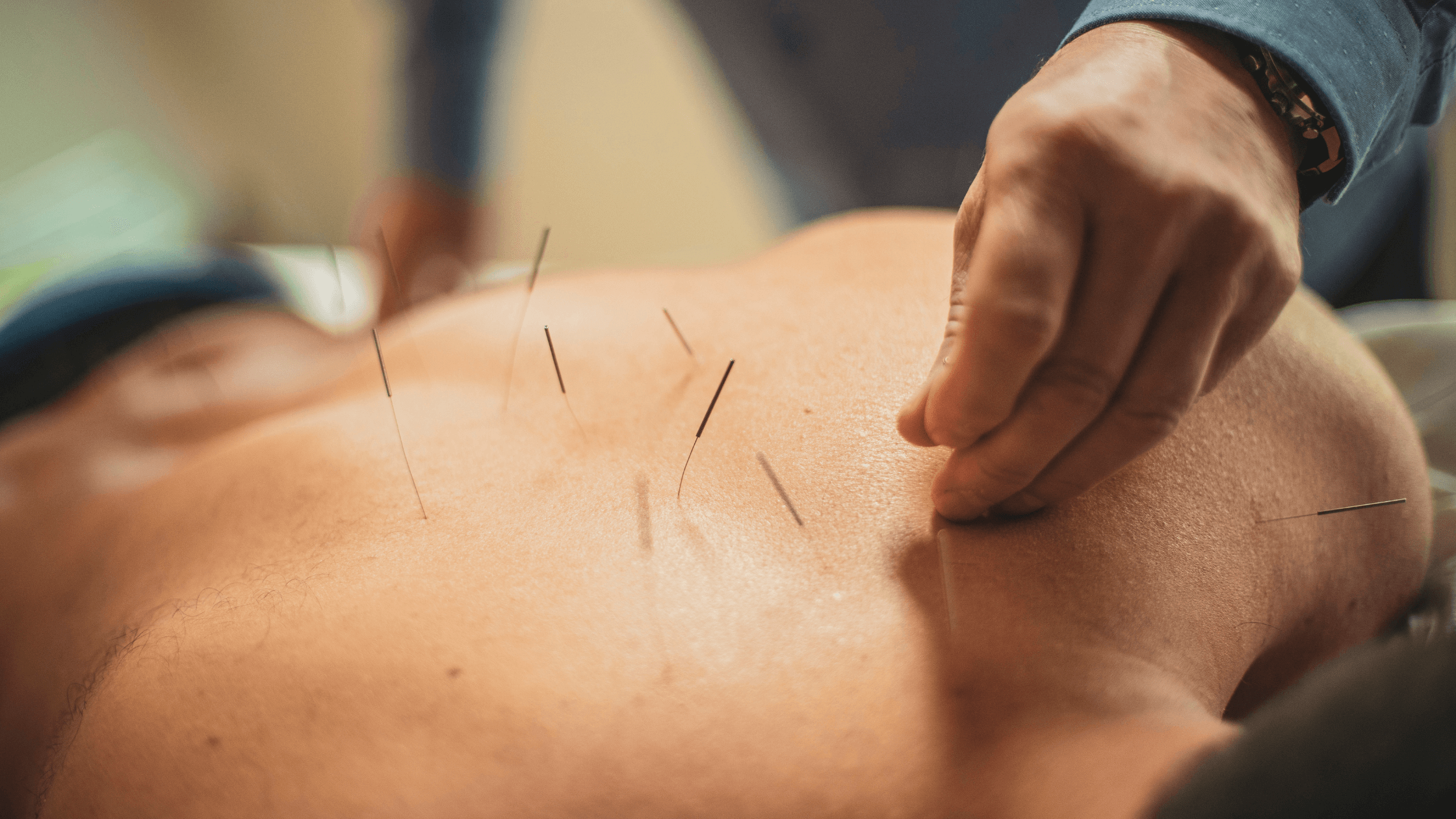
Working in the construction industry, you know your job can come with intense mental and physical demands. Construction work often involves repetitive strain, joint pain, stress, and sleep disturbances. Acupuncture has become an increasingly popular choice for relieving these symptoms, and there’s proven data to support the efficacy of this ancient practice.
Quick look
- Acupuncture is a Chinese practice dating back over 2,000 years, used to treat pain and improve overall wellness.
- This ancient practice involves using thin needles to stimulate specific points in the body, promoting balance and energy flow.
- Acupuncture may help lessen physical pain, reduce stress and anxiety, and make it easier to fall asleep.
- Speak with your doctor if you have a bleeding disorder or implants, take blood thinning medication, or are pregnant since these factors may make acupuncture a risky choice for you.
The origins of acupuncture
Acupuncture dates back to 2500 BC and is often credited to the Chinese Emperor Huangdi. References to acupuncture are often found in ancient Chinese medical texts. Acupuncture was initially used to address many health concerns, but it has continued to evolve over the centuries since. Today’s acupuncture practices have blended traditional wisdom and modern medical insights to create a trusted practice with science-backed benefits.
What is acupuncture?
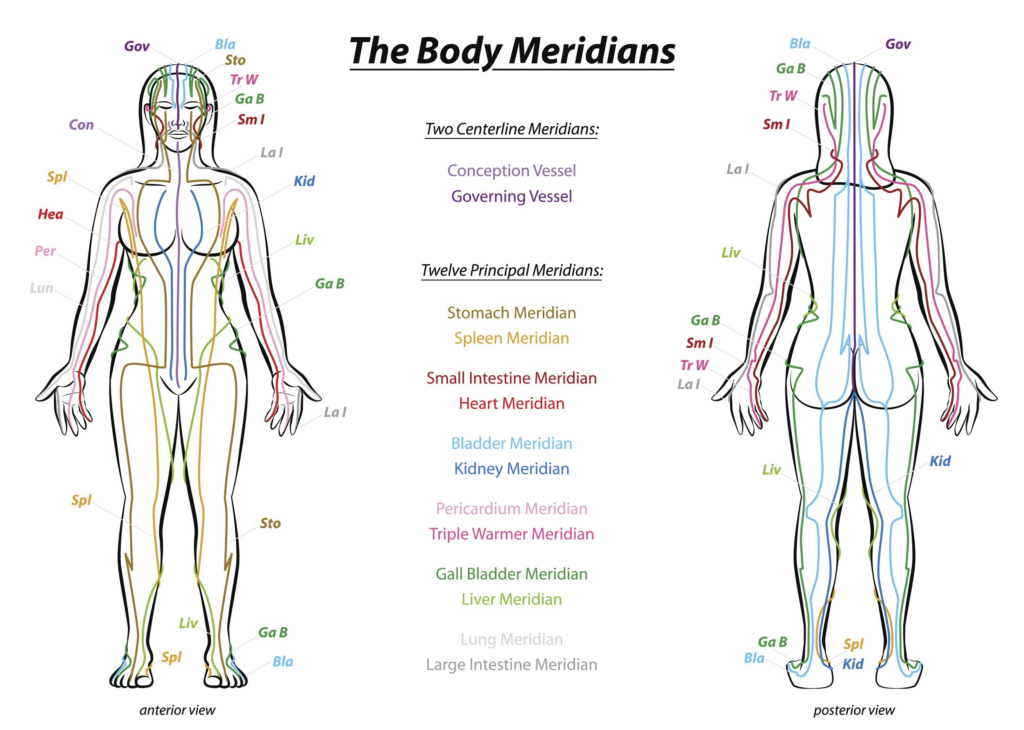
Acupuncture is a Chinese medicine practice that involves inserting extremely thin needles into over 2000 specific body points aligned with energy channels, or meridians. Acupuncture practitioners believe these meridians carry life’s force energy, qi (pronounced “chee”).
How does acupuncture work?
Acupuncture is based on the traditional Chinese medicine concept of Qi—energetic vitality that flows along the meridians in your body. There are 12 major meridians, each corresponding to different body organs or systems. When these pathways are blocked, Qi can’t move freely around the body, creating imbalances that lead to pain, discomfort, and disease. It’s believed that acupuncture can help release these blockages, which helps restore balance and energy flow throughout the body.
Acupuncture sessions can last up to an hour. Typically, the practitioner inserts the needles into the acupuncture points corresponding to your specific needs and then leaves them inserted. The needles are thin, so most people don’t find the process painful, and some even find it relaxing.
Electro-stim acupuncture
Electro-stim acupuncture is a modernized version of the traditional practice that involves attaching a mild electrical current to the acupuncture needles. This small current creates a tingling sensation and is often used to relieve muscle tightness, pain, and tension. The combination of Eastern medicine to address blocked energy and Western medicine to loosen tight muscles makes it an attractive choice for those with physically demanding jobs, like workers in the AEC space.
Alternatives to acupuncture needles
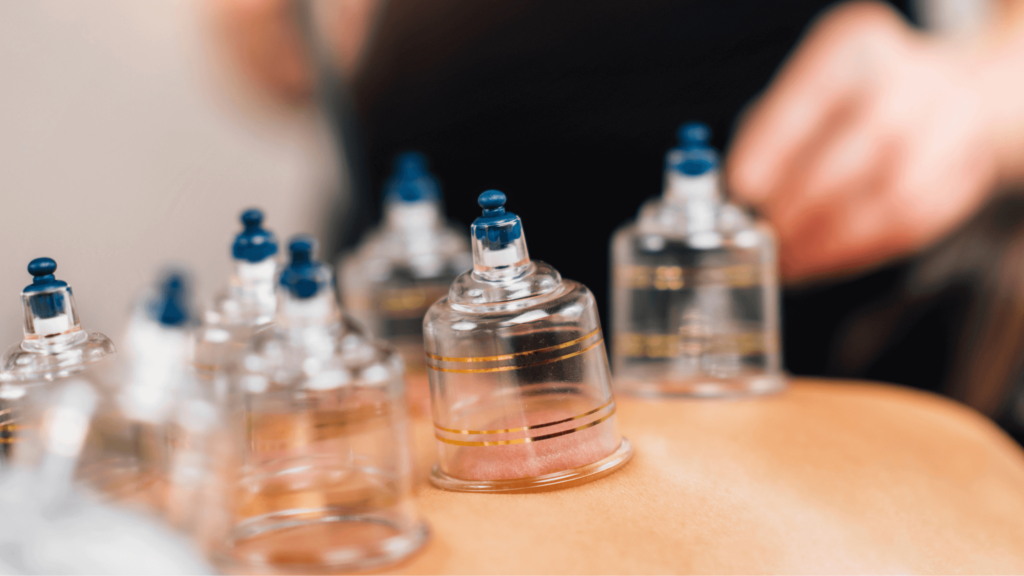

If you have an aversion to needles, the thought of having several of them inserted in various points of your body might be unbelievably unappealing. Luckily, there are other ways to access some of the benefits of acupuncture.
- Heat (moxibustion) involves burning an herb called Artemisia vulgaris (or mugwort) and holding it close to the skin near acupuncture points. Moxibustion practitioners believe that the warmth helps stimulate the flow of Qi, as acupuncture does, so you can tap into its benefits without the needles.
- Pressure (acupressure) involves firm pressure on acupuncture points to stimulate them without needles and help remove Qi blockages.
- Friction involves rubbing specific points on the skin to encourage blood flow and Qi circulation.
- Suction (cupping) uses cups made of glass or flexible silicone to create suction against the skin, which helps loosen the fascia, relieve muscle tension, and improve blood circulation.
Dry needling vs. acupuncture
Many people confuse dry needling with acupuncture. While the two practices share some similarities, they also have several notable differences.
In dry needling, thin needles are inserted into tight or painful muscle knots, called trigger points, to release muscle pain and tension. Dry needling is a Western medicine practice that focuses on muscular issues rather than the energetic flow of Qi addressed in acupuncture.
What are the benefits of acupuncture?
Construction can be a significant cause of physical strain and mental stress. Acupuncture is a great option for anyone who wears a hard hat and has been shown to relieve everything from migraines to insomnia.
Mental health
Studies have shown that acupuncture can help reduce stress and anxiety, which can be helpful for those working in high-pressure environments like construction.
Pain
Studies have shown that acupuncture can be effective in relieving various types of pain, including back pain, osteoarthritis, and muscle soreness—common complaints among people working physically demanding jobs. Research has also proven that acupuncture is an effective treatment for chronic pain.
Insomnia
Can’t sleep? Acupuncture may help. Many people find that acupuncture helps improve sleep quality, and it can be particularly beneficial if you struggle with insomnia due to stress or physical discomfort. Studies have shown that acupuncture is an effective treatment for reducing insomnia.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Acupuncture can reduce pain and inflammation in those with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), providing a noninvasive option for managing symptoms. A meta-analysis of over 40 studies concluded that acupuncture is a helpful treatment for RA sufferers.
Migraines
If you’ve ever suffered from migraine, you know that you’ll try just about anything to get rid of the headaches, nausea, brain fog, and postdrome hangovers—even if it involves getting stuck with needles. Luckily, acupuncture has been studied for its ability to treat migraine. In fact, one meta-analysis looked at over 3000 study participants and showed that acupuncture reduced migraine symptoms more than medication.
Who shouldn’t use acupuncture?
Acupuncture has been studied extensively, and while it’s a helpful treatment for many different conditions, it isn’t safe for everyone. Avoid acupuncture or discuss it with your doctor if you have one or more of the following conditions.
Bleeding disorders or a condition that requires you to take blood thinners: Acupuncture involves inserting needles into the skin, and while this is generally well-tolerated, there is still a risk of minor bleeding or bruising. If you have a bleeding disorder like hemophilia or you’re taking blood-thinning medications, you should approach acupuncture with caution.
Pregnancy: Several acupuncture points are known for stimulating uterine contractions, so if you’re pregnant, you should talk to your doctor and let your acupuncture practitioner know before your appointment.
Pacemakers: The electro-stimulation style of acupuncture might interfere with the function of pacemakers, so if you have one, you should avoid this type of acupuncture in favor of traditional acupuncture or a non-electrical version.
Implants: If you have breast implants or any other body implant, you should not have acupuncture near the implant site. Let your practitioner know before your appointment, and discuss with your doctor to ensure the treatment is safe for you.
Eastern medicine, global benefits
Acupuncture can be an effective treatment for everything from muscle pain to insomnia. Those in construction experience a massive amount of physical and mental stress, and this adds up over time. Whether you believe in Qi or the science-backed benefits, acupuncture can help lessen the load and shift the needle towards better health.
Want to read more ways to maintain a healthy mind and body in the construction industry? Sign up for our weekly newsletter!