3D modeling has changed how architects, engineers, and construction professionals design and build. It allows for highly detailed digital representations of structures, making planning and execution more precise. In the AEC industry, 3D modeling improves collaboration, reduces errors, and speeds up project timelines. It also enhances visualization, helping stakeholders see the final product before construction begins. With a growing number of software tools available, such as SketchUp, AutoCAD, and SolidWorks, 3D modeling is becoming a standard in modern construction projects.
Quick look
- 3D modeling creates digital representations of buildings, improving accuracy and design flexibility.
- It streamlines workflows by allowing real-time collaboration and better communication among teams.
- Different types of 3D modeling include BIM, parametric modeling, and mesh modeling.
- The benefits of 3D modeling include improved precision, faster project timelines, and cost savings.
- Top software options for AEC professionals include SketchUp, Rhino, AutoDesk, and Revit.
What is 3D modeling in the AEC industry?
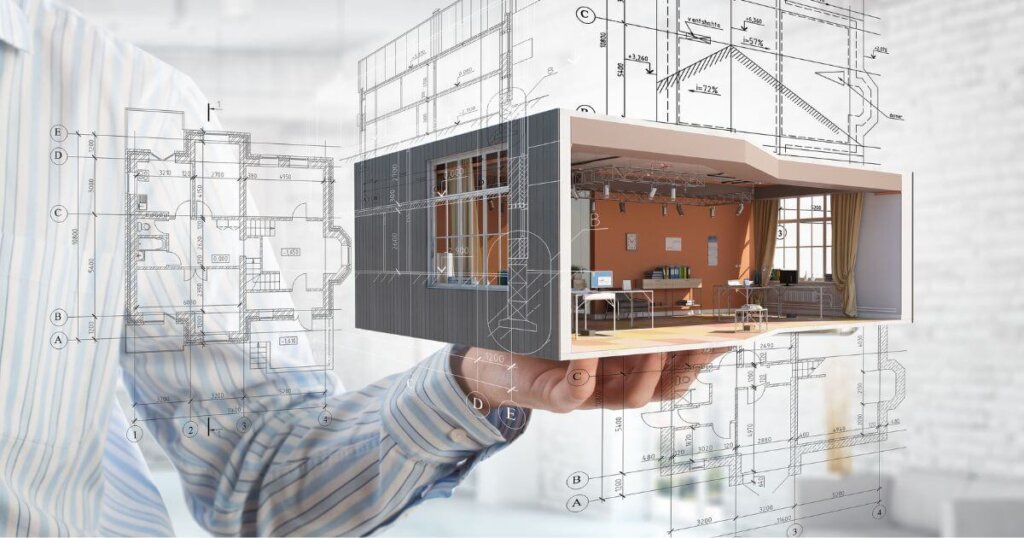

3D modeling in the AEC industry involves creating digital structures that replicate real-world buildings before construction begins. These models allow professionals to analyze structural integrity, materials, and design elements before breaking ground. Unlike traditional 2D blueprints, 3D models offer depth, making it easier to visualize spaces and detect potential design flaws early in the process.
This technology is widely used in architecture, engineering, and construction to improve planning accuracy and team communication. Architects can use 3D models to refine designs, engineers can assess load-bearing elements, and contractors can streamline material estimates. AEC professionals also use these models to simulate different conditions, such as lighting and airflow, ensuring a building functions efficiently before it’s built.
How 3D modeling works
3D modeling software generates detailed representations of structures using mathematical and geometric data. Designers start with basic shapes and refine them using tools that adjust dimensions, textures, and structural components. These models can be manipulated from any angle, making it easy to inspect details that might be overlooked in 2D plans.
Advanced 3D modeling methods incorporate real-world physics, helping engineers assess how materials and forces interact. Some models integrate with augmented reality (AR) or virtual reality (VR), allowing stakeholders to experience the building in an immersive digital space. This helps decision-makers understand layouts and functionality before construction begins, reducing costly changes later in the project.
Types of 3D modeling in construction
BIM
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a data-rich form of 3D modeling used for planning, designing, and managing construction projects. It integrates information about materials, costs, and timelines into a single model, making collaboration more efficient. BIM also supports clash detection, identifying conflicts between systems like plumbing and electrical before installation. Many AEC firms use BIM to streamline workflows and enhance project coordination.
Parametric modeling
Parametric modeling allows designers to set specific parameters that dictate how different components of a model behave. Changes to one element automatically update related elements, maintaining design consistency. This approach is useful for complex structures, where small adjustments can have cascading effects. It also helps optimize designs for efficiency, reducing material waste and improving construction accuracy.
Solid modeling
Solid modeling creates precise, mathematically defined 3D objects, making it ideal for structural analysis. Unlike surface modeling, which focuses on external appearances, solid modeling ensures objects have mass and volume. This is particularly useful in engineering applications, where strength and stability are critical considerations.
Mesh modeling
Mesh modeling represents surfaces as a collection of interconnected polygons. While commonly used for visual renderings and animations, it also plays a role in architectural visualization. Designers use mesh models for conceptual presentations, allowing clients to see realistic previews of a structure’s exterior.
Benefits of 3D modeling
1. Enhance precision and accuracy
3D modeling reduces human error by allowing designers to verify measurements, alignments, and spatial relationships before construction starts. Unlike traditional 2D drawings, digital models provide a clearer representation of dimensions and design elements, minimizing misinterpretations.
By detecting potential conflicts between structural components, MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) systems, and architectural features, 3D modeling prevents costly rework. Construction teams can rely on precise data to ensure materials are cut and assembled correctly, reducing material waste. This higher level of accuracy leads to fewer mistakes on-site, saving both time and money while improving overall project quality.
2. Streamline design and construction processes
With 3D modeling, multiple teams can collaborate seamlessly on the same project in real-time, eliminating the delays caused by outdated paper blueprints. Architects, engineers, and contractors can make adjustments to the design instantly, ensuring that all stakeholders are working with the most current version. This prevents miscommunication and costly design conflicts that could arise later in the construction phase.
The ability to simulate different construction scenarios also helps teams plan for potential challenges ahead of time. By reducing workflow disruptions and improving coordination, 3D modeling keeps projects on track and within budget.
3. Improved visualization
Stakeholders can see realistic representations of a building’s layout, materials, and finishes before construction begins. This level of detail helps architects and designers refine aesthetics, ensuring that the final product aligns with the client’s vision. With virtual walkthroughs and renderings, decision-makers can easily identify design flaws or areas that need improvement, making adjustments early rather than during construction.
Clients and investors who may not have technical expertise can better understand the design, leading to faster approvals and increased confidence in the project. The ability to present a visually compelling model also helps secure funding and stakeholder buy-in.
4. Cost savings
By detecting errors early in the design process, 3D modeling reduces costly rework and unexpected construction changes. Optimizing material use through precise modeling helps prevent over-ordering or unnecessary waste, directly cutting project costs. Fewer on-site modifications mean fewer delays, allowing projects to stay within their planned budget and timeline.
Additionally, digital simulations help teams assess the most cost-effective building methods, identifying potential savings on labor and materials. Over the long term, the efficiency gained through 3D modeling results in significant financial benefits for developers and construction firms.
5. Better project coordination
3D models integrate all construction elements, ensuring structural components, HVAC, electrical, and plumbing systems fit together without conflicts. This prevents costly on-site clashes that could lead to redesigns, work stoppages, or material waste. The ability to layer different trades within a digital model ensures that every team is aligned before construction starts.
With cloud-based platforms, project managers can oversee progress in real-time, making adjustments as needed to maintain efficiency. The improved coordination that comes with 3D modeling leads to smoother workflows and fewer last-minute surprises.
6. Risk reduction
Simulating construction scenarios in a digital environment helps identify safety concerns before they become real hazards on the job site. Potential risks, such as structural weaknesses or load-bearing miscalculations, can be addressed before materials are ordered or labor is scheduled.
By testing different building strategies, teams can determine the safest and most efficient construction approach. This reduces the likelihood of workplace accidents, which can lead to costly delays, liability issues, or regulatory fines. Ultimately, 3D modeling enhances site safety while improving efficiency and compliance with industry standards.
Top 3D modeling software for AEC workers
SketchUp
SketchUp is known for its user-friendly interface and powerful modeling capabilities, making it a favorite among architects and designers. Its intuitive tools allow users to create detailed 3D structures quickly without a steep learning curve. The software also features an extensive library of pre-built models, enabling users to incorporate furniture, materials, and structural components with ease.
SketchUp also supports a wide range of plugins that enhance functionality, from rendering tools to energy analysis extensions. Whether for early-stage conceptual design or final presentations, SketchUp provides flexibility and efficiency for AEC professionals.
Rhino
Rhino is popular for its ability to handle complex geometric shapes with high precision, making it an excellent choice for architectural and industrial design. The software’s advanced modeling tools allow users to create intricate freeform structures that would be difficult to achieve with traditional CAD programs. Rhino’s versatility makes it useful for both early-stage design and detailed technical modeling, offering compatibility with various file formats.
Its integration with Grasshopper, a visual programming tool, further expands its capabilities by allowing parametric and algorithmic design processes. This makes Rhino an essential tool for architects and engineers working on projects that require creative, non-traditional designs.
AutoDesk Revit
Revit is a leading BIM software that integrates design, visualization, and documentation into a single platform, making it indispensable for large-scale construction projects. It allows architects, engineers, and contractors to collaborate seamlessly by sharing a central model that updates in real-time. One of its key strengths is parametric modeling, which enables users to make intelligent design adjustments that automatically update related components.
Revit also excels in clash detection, identifying conflicts between structural, mechanical, and electrical systems before construction begins. This reduces errors and streamlines project execution, making Revit a critical tool for modern AEC workflows.
AutoCAD
AutoCAD remains a staple in the AEC industry for both 2D drafting and 3D modeling, offering precision and control for technical drawings. Many architects and engineers rely on it for detailed floor plans, elevations, and sections that serve as the foundation for construction projects. Its powerful drafting tools allow for efficient documentation, while its 3D modeling capabilities enable the creation of realistic visualizations.
AutoCAD also supports custom automation through scripts and macros, helping users speed up repetitive tasks. Often used alongside other modeling software like Revit or SketchUp, AutoCAD remains a key component of many AEC professionals’ toolkits.
SolidWorks
SolidWorks is favored in engineering and structural design for its solid modeling capabilities, allowing users to create highly detailed, parametric 3D models. Unlike surface-based modeling programs, SolidWorks provides precise representations of objects with mass and volume, making it ideal for structural analysis. Engineers use it to test designs under real-world conditions, simulating factors such as load distribution and material strength.
The software’s built-in simulation tools help identify potential weaknesses before construction begins, reducing the risk of costly errors. With its ability to integrate with other engineering and manufacturing software, SolidWorks is a valuable asset for professionals working on complex, performance-driven projects.
Bottom line
3D modeling is a game-changer in the AEC industry, making design and construction more efficient, accurate, and cost-effective. As the technology continues to improve, it’s becoming an essential tool for architects, engineers, and contractors.
To stay updated on the latest trends in construction and technology, subscribe to our newsletter at Under the Hard Hat and follow us on social media.


1 comment