It’s well-known that we are in a race against time when it comes to saving our planet from the damaging effects of climate change. The global push to address this crisis has increasingly focused on the construction environment. With nearly 40% of global carbon dioxide emissions linked to buildings, the industry is one of the biggest contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. To counteract climate change and decarbonize the construction industry, companies can advocate for policy changes that support sustainable building practices, invest in carbon offset programs, and adopt modular construction.
The link between buildings and climate change

According to the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), building operations and construction are significant drivers of carbon dioxide emissions, contributing almost 40% of the global total. This includes emissions generated from both the construction of buildings and their ongoing operation, such as heating, cooling, and lighting. The construction sector, in particular, is responsible for a large portion of these emissions, driven by the extensive use of energy-intensive materials like steel, cement, and glass.
As urbanization accelerates rapidly around the world, the demand for new construction continues to rise, leading to even greater emissions. Without substantial changes in how buildings are constructed and managed, this sector will continue to be a major contributor to climate change, pushing the world further away from meeting international climate goals.
Decarbonizing the construction industry
Decarbonizing the construction industry is crucial to reducing its environmental impact. But we must consider carbon emissions not only in the construction phase. This effort involves minimizing carbon emissions throughout the building’s entire lifecycle, from material production to demolition.
One of the most effective strategies is the use of low-carbon building materials, such as sustainable timber or recycled steel, which can significantly reduce the carbon footprint compared to traditional materials.
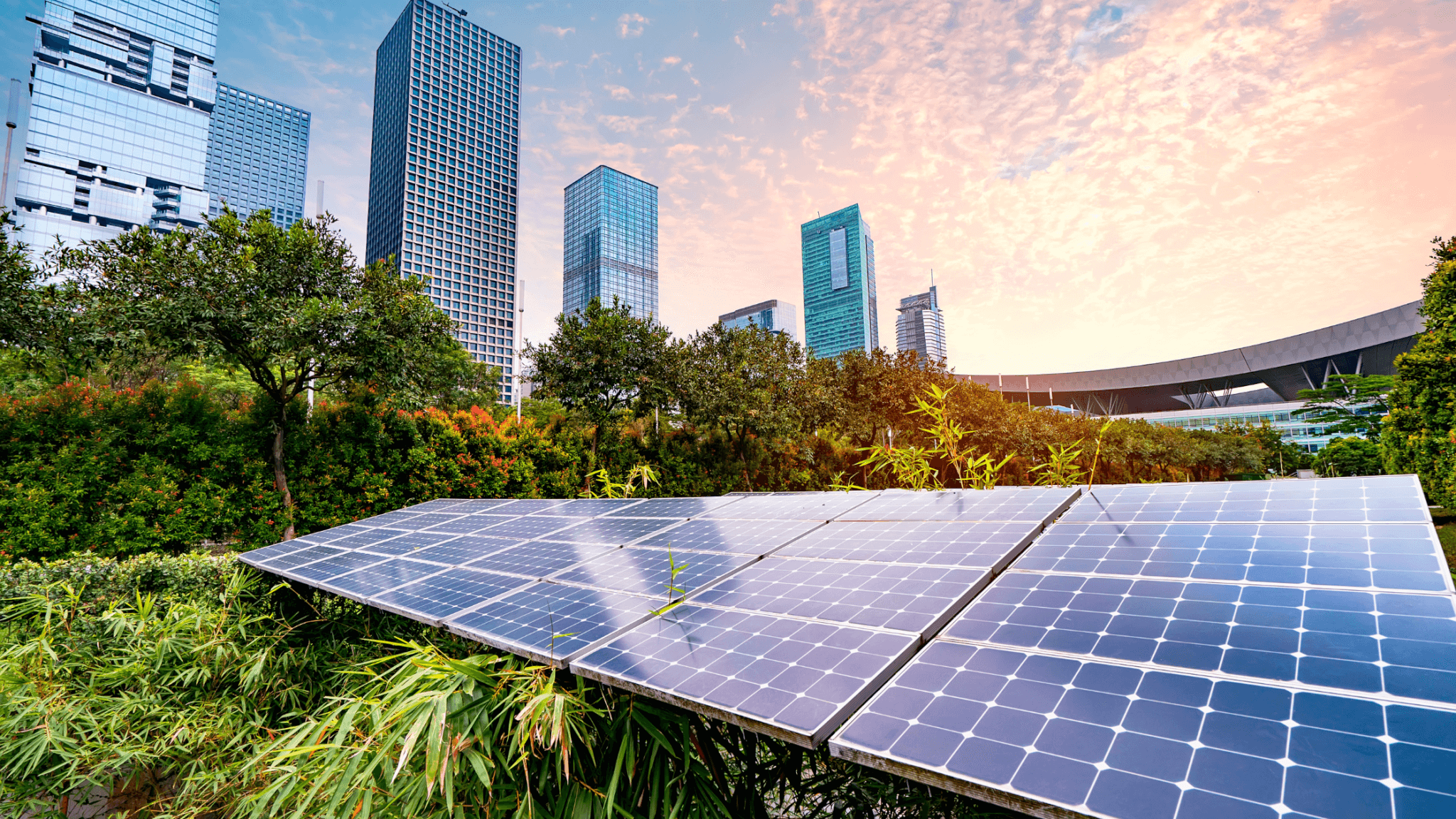
The UNEP’s Global Status Report for Buildings and Construction highlights the importance of shifting towards energy-efficient designs and integrating renewable energy sources. For example, the incorporation of solar panels and wind energy systems can drastically reduce a building’s reliance on fossil fuels.
Additionally, the electrification of construction equipment—replacing diesel-powered machinery with electric alternatives—can reduce emissions during the building process.
Electrification isn’t the only solution, though; optimizing energy efficiency in building design is crucial. Passive design strategies, like natural ventilation, daylighting, and thermal insulation, can reduce a building’s energy demand, thus lowering operational emissions. Over time, this switch can make a big difference in the environment.
Adopting a circular economy approach in construction—where materials are reused and recycled—can minimize waste and reduce the need for new resources, further cutting emissions.
Another promising avenue for decarbonizing construction is the adoption of bio-based materials, such as hempcrete and bamboo. These materials not only sequester carbon during their growth but also require less energy to produce compared to conventional materials. These innovative materials can serve as viable alternatives to energy-intensive options like concrete and steel, further reducing buildings’ carbon footprints.
How construction companies can reduce carbon emissions
Construction companies play an important role in the effort to reduce carbon emissions.
- Embracing green building certifications: Certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) and BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method) can help companies ensure their projects meet high standards of sustainability. These certifications often require the use of energy-efficient technologies, water-saving fixtures, and sustainable materials, all of which contribute to lower emissions.
- Adoption of modular construction techniques: These involve prefabricating building components off-site and then assembling them on-site. This method reduces material waste and shortens construction timelines, leading to lower energy use and emissions.
- Invest in carbon offset programs: These programs help balance out any remaining emissions from their projects.
- Advocate for policy changes that support sustainable construction practices: Governments can incentivize green building through tax breaks, grants, and other financial incentives, making it easier for companies to adopt these practices.
- Integrating new technology: Digital tools like Building Information Modeling (BIM) allow for more accurate planning and resource management, helping to reduce waste and optimize energy use. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will play an increasingly important role in helping construction companies achieve their carbon reduction goals.
Bottom line
Green buildings are an essential component in the fight against climate change, offering a way to significantly reduce the environmental impact of the built environment. However, they are not a silver bullet. The construction industry must adopt a holistic approach to decarbonization, encompassing everything from material selection to energy use and waste management.
By embracing sustainable practices and incorporating new technologies, the construction sector can play a leading role in the global effort to combat climate change. The transition to green buildings is not just about meeting regulatory requirements or achieving certification—it is about redefining the way we think about the construction environment and its impact on our planet. As more companies and governments commit to this transition, the potential to make a meaningful difference in the fight against climate change becomes increasingly real.


1 comment