The pelvic floor is vital to women’s health, supporting essential functions like bladder control, spinal stability, and sexual wellness. This network of muscles is often overlooked but is crucial for women in physically demanding professions like construction and the skilled trades. Incorporating exercises such as lunges, deep squats, and pelvic tilts into your routine can help strengthen these muscles, improving core stability and reducing the risk of injury.
The power of the pelvic floor
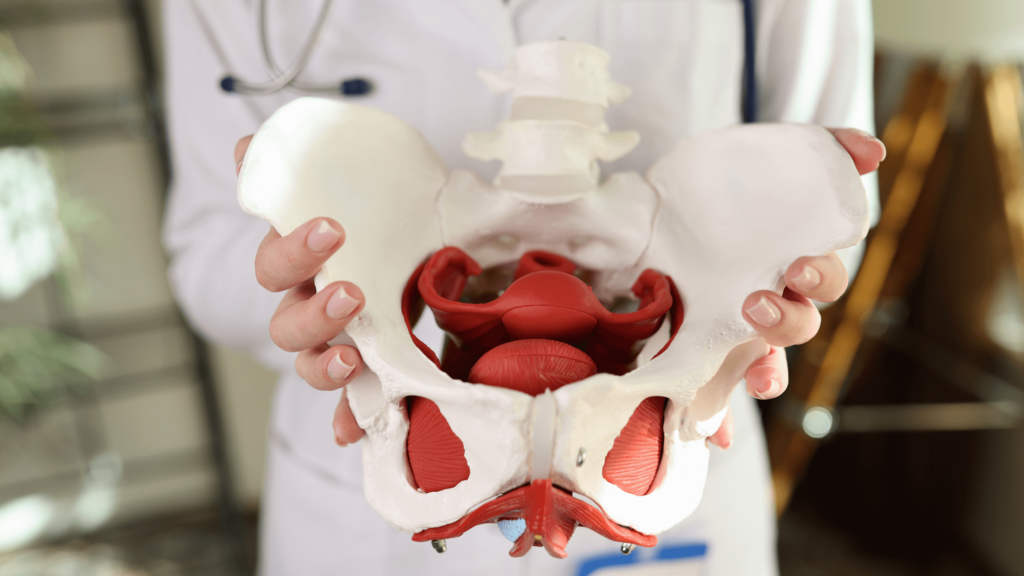
The pelvic floor is a group of muscles and connective tissues located at the base of the pelvis. These muscles form a supportive sling that helps keep vital organs in place while also playing a critical role in bladder control, core stability, and sexual health. Though commonly associated with childbirth recovery, pelvic floor health is essential for all women, regardless of age or life stage. Women in construction and trades, in particular, often perform tasks like lifting heavy objects and repetitive bending, which place added strain on this area, making it even more important to maintain strength.
Muscles in the pelvic floor
The pelvic floor is composed of three key muscle groups:
- Levator ani: This includes the pubococcygeus, iliococcygeus, and puborectalis muscles, which work together to support the pelvic organs and control bowel and bladder functions.
- Coccygeus: A smaller muscle that stabilizes the tailbone and contributes to pelvic floor support.
- Deep perineal pouch: These smaller muscles aid in urinary and reproductive functions.
Together, these muscles coordinate with the core and diaphragm, creating a dynamic support system for the lower body.
Functions of the pelvic floor
Support pelvic organs
The pelvic floor acts as a foundation for the bladder, uterus, and rectum. Strong pelvic floor muscles hold these organs in place, preventing issues like pelvic organ prolapse, where organs may shift downward due to weak support. This condition can cause discomfort, pain, and urinary incontinence, especially in women whose jobs involve heavy lifting. For tradeswomen, strong pelvic floor muscles help safeguard against these complications, ensuring long-term health and comfort.
Stabilize the pelvis and spine
The pelvic floor plays a significant role in core stability, working alongside the abdominal and back muscles to stabilize the pelvis and spine. This stabilization is essential for maintaining posture, reducing the risk of lower back pain, and performing physically demanding tasks safely. For women in construction, whose jobs often require twisting, lifting, and prolonged standing, a strong pelvic floor acts as a built-in support system, preventing injuries and improving overall mobility.
Assist with sexual function
Pelvic floor muscles play a direct role in sexual health by supporting the vaginal walls and improving blood flow to the area. Strong muscles enhance sensation and improve muscle control, contributing to a better sexual experience. A healthy pelvic floor also reduces the risk of discomfort or pain during intimacy, promoting both physical and emotional well-being.
Support bowel and bladder control
One of the most well-known functions of the pelvic floor is its role in bowel and bladder control. These muscles help regulate the release of urine and stool, preventing incontinence. Women in construction often work in environments with limited restroom access, making strong pelvic floor muscles particularly valuable for maintaining control and comfort throughout the workday.
Pelvic floor disorders
Pelvic floor disorders occur when the muscles become too weak, too tight, or unable to function correctly. Weakness often results from factors like pregnancy, childbirth, aging, obesity, or repetitive heavy lifting. Tightness, on the other hand, can stem from chronic stress, poor posture, or trauma. Both conditions can lead to symptoms such as urinary incontinence, pelvic pain, and bowel control issues.
Tradeswomen, in particular, are at risk of developing pelvic floor disorders due to the physical demands of their work. Improper lifting techniques, prolonged standing, and repetitive strain can exacerbate these issues over time. Pelvic floor dysfunction may also result in pelvic organ prolapse, where weakened muscles allow organs to shift downward, causing significant discomfort.
Recognizing the early signs—such as frequent urinary leaks, a sensation of heaviness in the pelvis, or pain during intercourse—is key to seeking appropriate treatment. Pelvic floor therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and targeted exercises can help address these concerns, restoring strength and functionality.
8 exercises to strengthen your pelvic floor
The following exercises are effective alternatives to traditional Kegels. They target the pelvic floor and surrounding muscles, improving core stability, strength, and overall functionality. These movements are particularly beneficial for women in physically demanding professions, providing a solid foundation for tackling everyday challenges.
1. Lunges
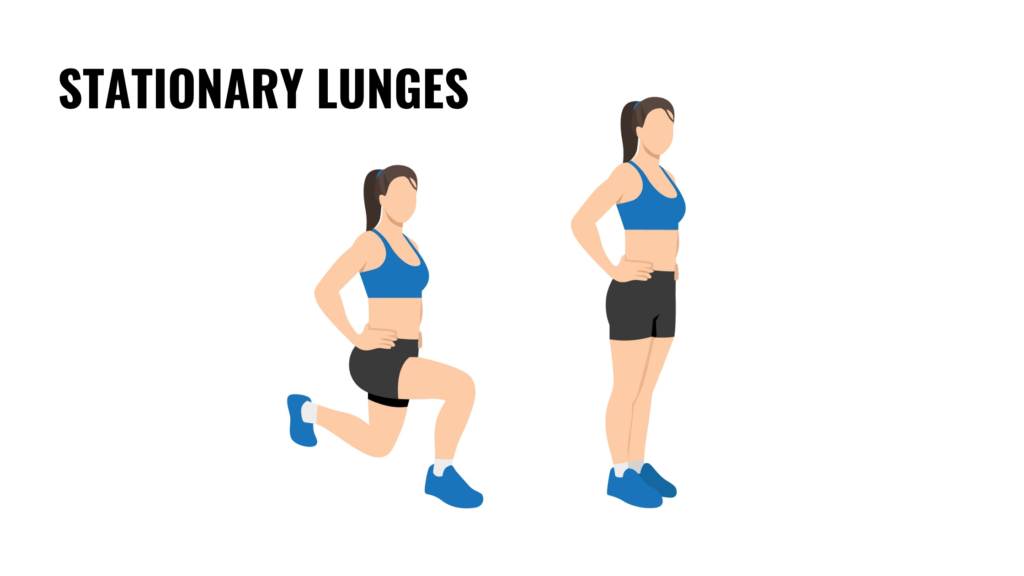
Lunges are a compound exercise that works the lower body while engaging the pelvic floor. Stand upright with feet hip-width apart. Step one foot forward, lowering your body until both knees form 90-degree angles. Keep your core engaged and focus on lifting your pelvic floor as you push back to the starting position. Repeat on the other side.
This movement strengthens the thighs, hips, and glutes, which are closely connected to the pelvic floor. It also improves balance and coordination, which are essential for tasks requiring stability, such as climbing ladders or lifting heavy objects.
2. Inner thigh squeeze with glute bridge
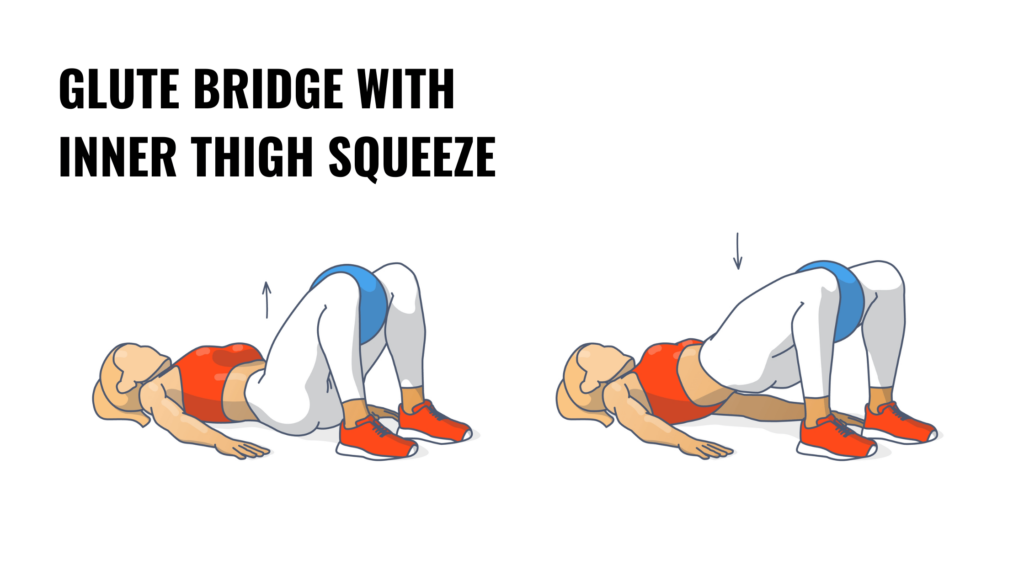
This exercise activates the inner thighs and glutes while engaging the pelvic floor. Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Place a small ball or cushion between your knees. Squeeze the ball as you lift your hips into a bridge position, focusing on engaging the pelvic floor at the top of the movement. Lower slowly and repeat.
The squeezing motion targets the adductor muscles, which support pelvic floor strength. The bridge element also strengthens the glutes, improving hip stability and reducing the risk of lower back strain during physical labor.
3. Deep squat
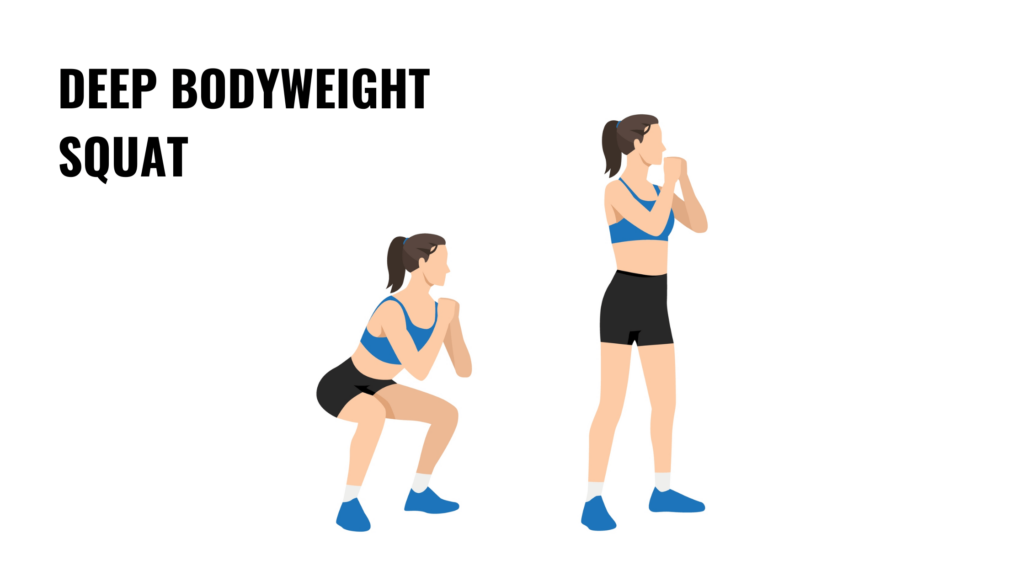
Deep squats are one of the best functional exercises for strengthening the pelvic floor. Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, toes slightly turned out. Lower your hips as if sitting in a chair, going as deep as your flexibility allows while keeping your chest upright and your core engaged. Push through your heels to return to standing.
This movement stretches the pelvic floor muscles while activating them to provide support. Deep squats also build strength in the legs and hips, enhancing mobility and reducing strain during repetitive bending or lifting.
4. Bird dog
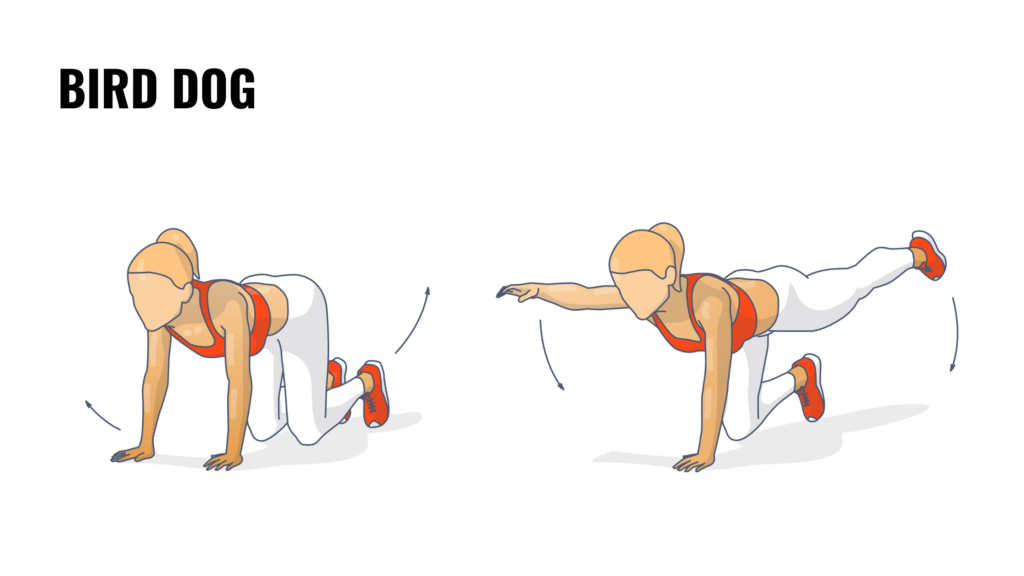
Bird dog is a core-stabilizing exercise that engages the pelvic floor. Start in a quadruped position with your wrists under your shoulders and knees under your hips, ensuring your spine remains neutral. Extend one arm and the opposite leg simultaneously, keeping your movements slow and controlled. Hold briefly, then return to the starting position and switch sides.
This exercise improves balance and coordination while strengthening the pelvic floor, core, and lower back. It’s particularly useful for preventing strain and injuries in women performing repetitive physical tasks.
5. Pelvic tilts
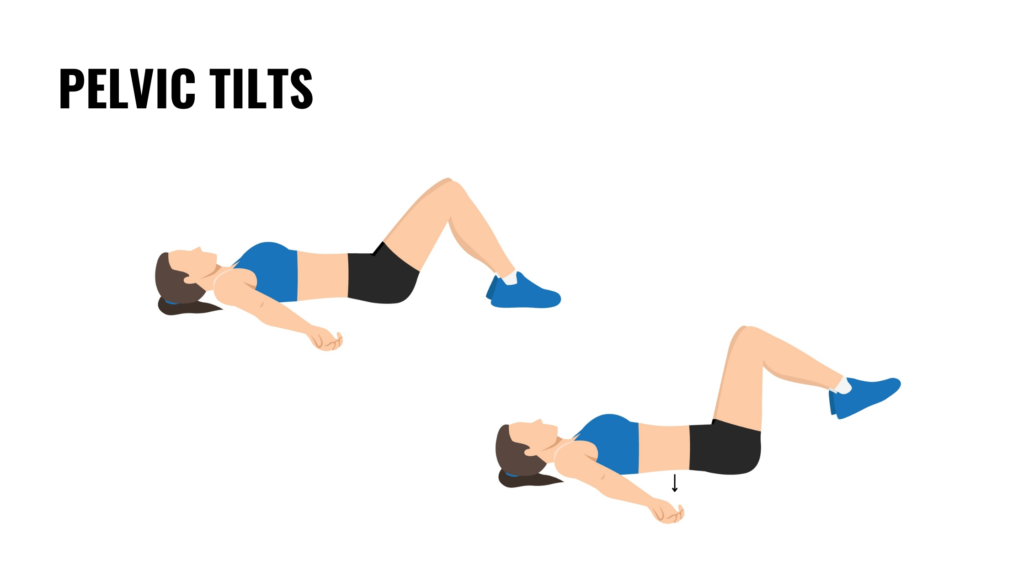
Pelvic tilts are a gentle way to activate the pelvic floor and relieve lower back tension. Lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat. Tilt your pelvis upward and push your lower back against the floor. Hold for a few seconds before releasing.
This exercise strengthens the pelvic floor and lower abdominal muscles, improving posture and reducing the risk of lower back pain. It’s ideal for beginners or anyone recovering from an injury.
6. Dead bugs
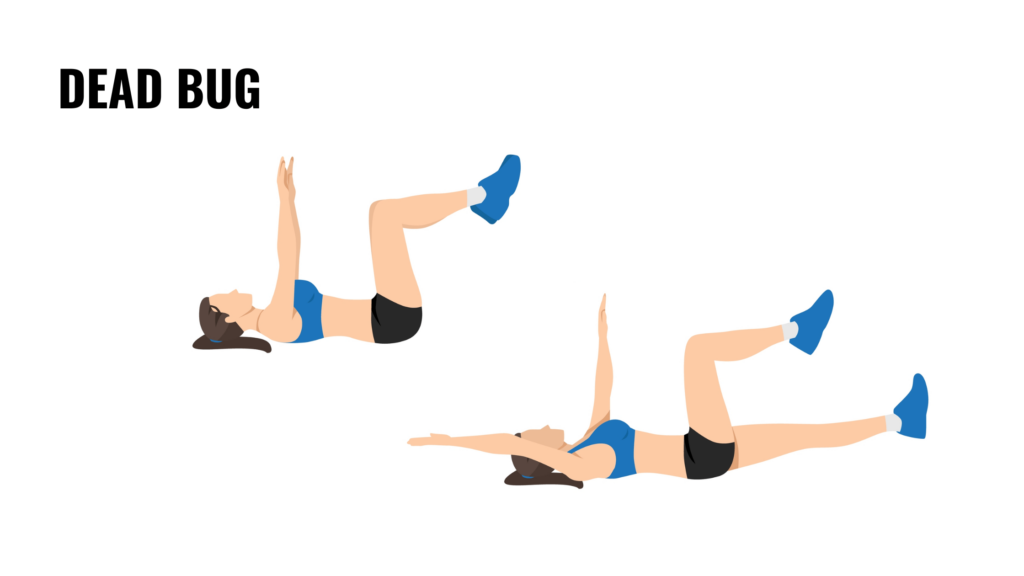
Dead bugs are a great core-strengthening exercise that also engages the pelvic floor. Lie on your back with your arms extended toward the ceiling and your knees bent at a 90-degree angle; your knees should align with your hips. Slowly lower one arm and the opposite leg toward the floor, keeping your core engaged and your lower back pressed into the mat. Return to the starting position and repeat on the other side.
This exercise improves coordination and core stability, both of which are essential for pelvic floor strength. Dead bugs mimic functional movements, making them particularly beneficial for women in construction who often work in awkward positions or carry heavy loads. Engaging the pelvic floor during this controlled movement strengthens the muscle group’s ability to support your spine and pelvis.
7. Side-lying leg lifts
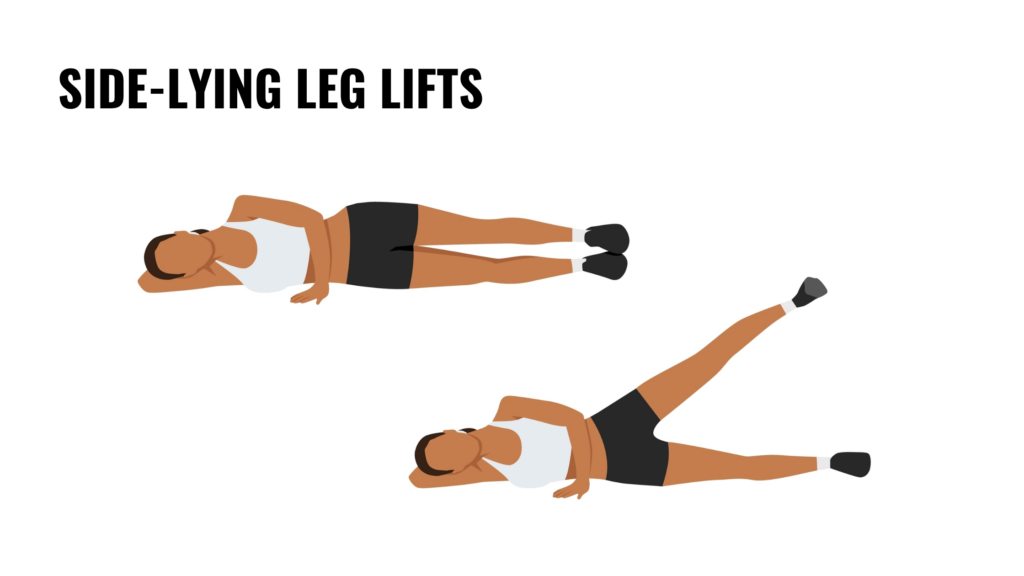
This exercise strengthens the gluteus medius, hips, and pelvic floor and improves overall stability. Lie on your side with your legs stacked and your body in a straight line. Rest your head on your lower arm and place your top hand on the floor in front of you for support. Slowly lift your top leg to about 45 degrees, keeping your foot flexed and your hips steady. Lower it back down with control and repeat.
Side-lying leg lifts help balance the muscles around the pelvis, which is crucial for pelvic floor health. Strong hips provide better support to the pelvic floor and reduce strain during lifting, bending, and other physically demanding tasks.
8. Standing heel raises
Heel raises are a simple but effective way to engage the pelvic floor while strengthening the calves and improving balance. Stand with your feet hip-width apart, holding onto a sturdy surface for support if needed. Slowly lift your heels off the ground, rise onto the balls of your feet, and focus on engaging your pelvic floor as you lift. Lower back down with control and repeat.
This exercise improves lower-body strength and coordination, helping reduce strain on the pelvic floor during daily activities. For women in trades who are often on their feet for long hours, heel raises can improve overall stability and prevent fatigue-related injuries.
Bottom line
Pelvic floor health is essential for women’s well-being, particularly those in physically demanding fields like construction. Incorporating targeted exercises into your fitness routine can strengthen this critical muscle group, improve core stability, and reduce the risk of injury or dysfunction.
For more tips on health and wellness in the trades, subscribe to our weekly newsletter and follow us on social media.


