One of the more prevalent, although often forgotten, hazards on construction sites is fire. To combat fire hazards head-on, companies have been recently leveraging safer practices and using more fire-resistant building materials. Buildings are being upgraded and fitted with high-performance fibers, bio-based materials, and more advanced coatings and treatments to maintain integrity and stability. Proper fire-resistant material is the key to stopping the spread of a fire.
Fire safety in construction
Between 2017 and 2021, fire departments across the U.S. responded to an average of 4,440 buildings under construction annually. These caused an average of $370 million in direct property damage per year, 59 civilian injuries, and 5 deaths. The construction fire rate has increased since 2014 after declining between 2006 and 2010.
Roughly 3 out of 4 of these fires involved residential properties, and the leading contributing factors included heat sources too close to combustible materials, electrical failures, and abandoned or discarded products.
There is no singular, truly fireproof building material, but advancements in well-constructed fire-resistant materials have resulted in less property damage and fewer injuries. Building damage is inevitable with fires, but the key is to build a structure where a fire would catch and escalate slowly, allowing more time to contain the fire and for occupants to escape.
This is how these new materials are rated: how long a fire would take to impact its structural integrity. Some heavy timber, for example, could be classified as fire-resistant according to this measure. In contrast, metals like steel and aluminum aren’t combustible but tend to buckle faster under intense heat.
What are fire-resistant materials?
Fire-resistant materials, not to be confused with fire-retardant materials, are made to withstand heat and resist burning. They are designed to maintain structural integrity and prevent flames from catching and escalating. Think of bunker gear or PPE worn by firefighters to protect them from fire.
On the other hand, fire-retardant materials, such as iron, plywood, brick, and concrete, are designed to burn slowly. While no material is entirely fire-proof, integrating fire-resistant and fire-retardant materials into building practices can mitigate the risk of significant losses.
Advancements in fire-proof building materials
Fire-resistant glass and steel rebar
Under extreme temperatures, regular steel can diminish and significantly impact the structural integrity of a building. Stainless steel rebar, however, is fire-resistant, more durable, and maintains its structural performance in the same conditions that deteriorate steel. Because of its reliability, steel rebar is expected to have the fastest-growing CAGR between 2023-2031.
Regular glass shatters quickly when exposed to high heat, but fire-resistant glass is made to withstand extreme temperatures and mitigate the spread of smoke and flame. This glass will maintain its structure for 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the quality. Ceramic glass, wired glass, and intumescent glass are just a few examples of several types of fire-resistant glass. They are crucial for containing fires in a particular area, giving building occupants more time to evacuate safely.
Intumescent coatings and paints

Intumescent paints and coatings are designed to swell at high temperatures, forming an insulated char layer and protecting the underlying material or substance from heat and flame damage. More recent advancements in these coatings involve nanotechnology, including nano-clays, graphene, and carbon nanotubes, which improve char strength, efficiency, and thermal stability.
New intumescent coatings also include ammonium polyphosphate, melamine, and pentaerythritol, which, when combined, create a more effective fire protection system. When applied to the undercoat of a new residential house or building, the paint creates a thick protective layer that deflects heat from bushfires and reduces the temperature at the substrate surface to approximately 30°C from 1000 to 1200°C. These advancements in intumescent coatings are pivotal for elevating fire safety standards.
Bio-based materials

Biomaterials from renewable sources, such as biopolymers and plant fibers, are being explored for their fire-resistant properties. Researchers have developed fire-resistant composites from flax, hemp, and jute combined with bio-based resins.
Australian scientists are also researching using fungi as a nontoxic, bio-based alternative to the more toxic flame retardants in building materials. So far, molasses-fed sheets of fungi have been successfully developed, and they could be used as a fire-resistant coating in construction or as a leather alternative.
These materials take advantage of the fire-resistant properties of mycelium, the root-like structure of fungi. This research could replace hazardous plastics and chemicals as a reliable fireproof material.
Advanced coatings and treatments
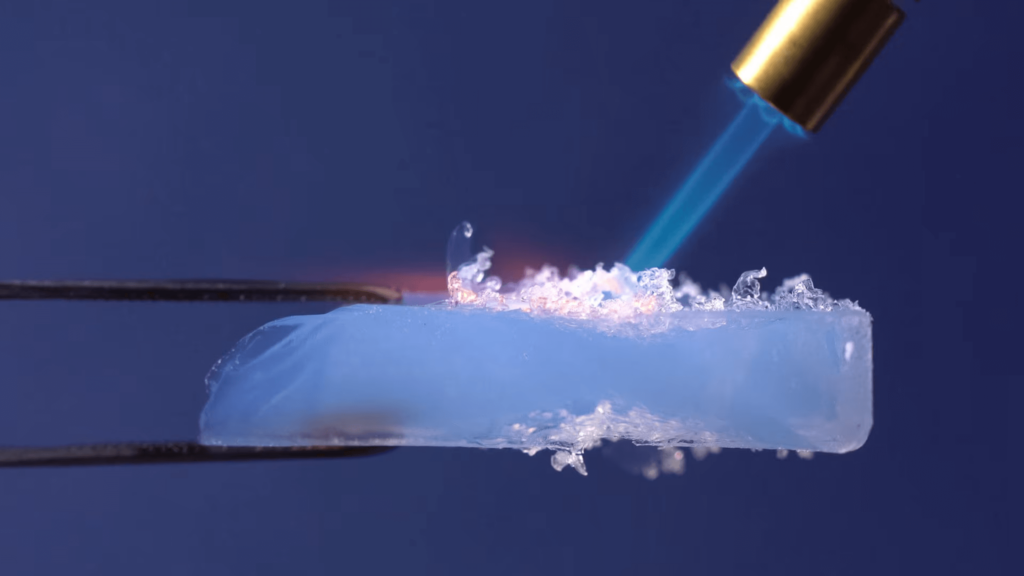

Aerogels, ceramic coatings, self-healing coatings, and hydrogels each protect against fire damage and serve a specific purpose. For example, ceramic coatings are designed explicitly for composite surfaces and metals to enhance their resistance to fire and extreme heat.
These advanced coatings typically consist of aluminum oxide or silicon carbide, creating a strong barrier that reflects heat and prevents structural damage. Silica aerogels, for instance, have been enhanced with fire-retardant additives to improve their flame resistance. These gels could be used in various construction applications, such as insulation and PPE.
Hydrogels are being categorized as an innovative solution for fire-resistant fabric treatment. They can be strategically applied as a coating to act as an effective char layer against flames. Recent research has been dedicated to elevating durability and reusability with some of these coatings. Using self-healing materials, these coatings can repair themselves after sustaining heat damage, which could ensure better long-term protective properties.
High-performance fibers
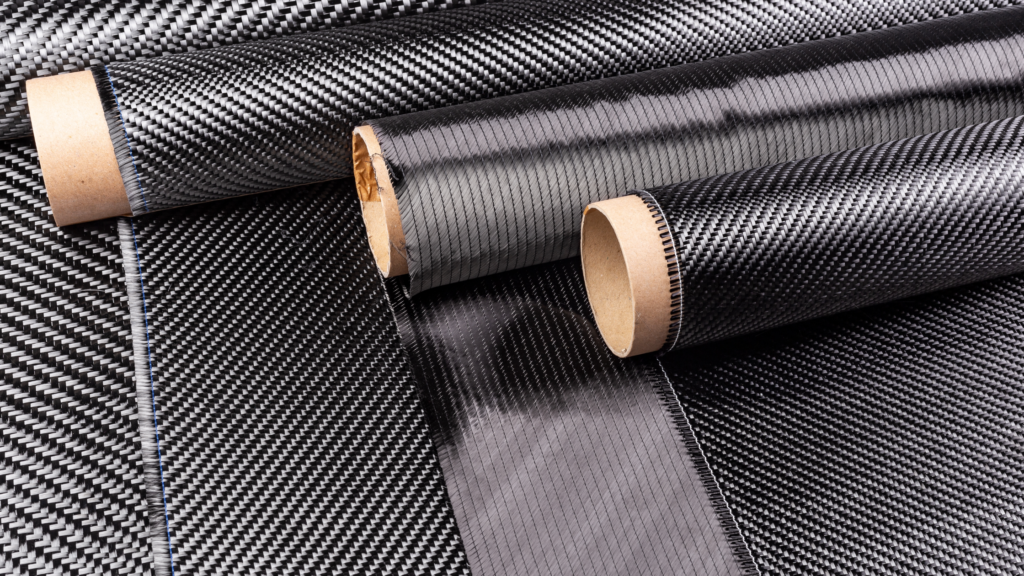

Polybenzimidazole (PBI), aramids, and poly(p-phenylene-2,6-benzobisoxazole) (PBO) are high-performance fibers that have become invaluable in applications that require extreme fire resistance. Aramis fibers like Nomex and Kevlar are renowned for their thermal integrity and fire resistance.
These fibers are often used in firefighting PPE, aerospace components, and combat and military applications. Aramids’ chemical processing and treatment advancements have significantly increased their flame-retardant properties and durability.
PBO and PBI fibers offer even greater fire-resistance qualities than aramids. PBI fibers don’t melt, making them ideal for hot environments. PBO fibers have superior thermal stability and are used for firefighters’ and industrial workers’ PPE. Fiber-reinforced polymers are gaining popularity due to their lightweight and excellent mechanical properties.
Smart materials
In a phase transition, phase-change materials absorb and dispel thermal energy, providing fire resistance and thermal regulation. When used and integrated into building materials, they can uphold structural integrity and lower temperature spikes in the event of a fire.
Thermochromic materials are designed to change color in response to temperature shifts, visually identifying heat exposure. These materials could be used in fabrics and coatings to monitor a fire risk. Thermoresponsive polymers shift their physical properties at a temperature change and are being explored for their potential advancement in fire protection.
The pros and cons of fire-resistant materials
Switching to more fire-resistant materials seems like the way forward, but there are a few things to consider.
Pros
- Sustainability: Bio-based materials to replace toxic plastics could provide the same fire resistance with less environmental impact.
- Improved performance: Upgrades in the compounds that make up sealants, glass, and rebar make more durable materials.
- Decreased risk of injury or fatality: The increased durability and fire resistance allow occupants to leave a building safely in the event of a fire.
- Decreased property damage: Stronger building coatings that protect the core structure mean more buildings that could be salvaged and easily fixed.
Cons
- Expensive: Some newer, stronger materials are often less available and could be more costly to order and implement.
- Less ventilation: Fire-resistant constructed roofs mean little to no ventilation.
- Time-intensive implementation: Switching to an improved fire-resistant building requires more training, slower implementation, and retroactive integration.
Bottom line
Construction fire safety is most effective when workers implement proper safety protocols. However, if a structure does catch fire, a fire-resistant material could be the difference between safety and fatality. Implementing more advanced materials like fire-resistant glass, intumescent coatings, and bio-based materials will make the projects more sustainable and stronger, preventing injuries and reducing potential property damage.
For more on safety in construction, subscribe to our weekly newsletter and follow us on social media.


