Renewable energy projects are scaling up in 2025, driven by urgent climate goals, energy security concerns, and rapid advancements in green technology. Governments and developers are investing heavily in large-scale solar, wind, and hydrogen infrastructure to meet decarbonization targets and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Projects like India’s Gujarat Hybrid Renewable Energy Park and the U.S.-based SunZia Wind and Transmission are setting new benchmarks for renewable energy.
The 11 largest renewable energy projects under construction
1. Gujarat Hybrid Renewable Energy Park

- Location: Vighakot, Kutch district, Gujarat, India
- Size/specs: 30 GW (solar and wind) across 72,600 hectares
- Expected timeline: Partial capacity online by late 2024; full completion by 2026
The Gujarat Hybrid Renewable Energy Park is set to be a global landmark in renewable energy infrastructure, targeting 30 GW of combined solar and wind power generation. Located in the vast and sun-scorched expanse of the Rann of Kutch, the park spans over 72,600 hectares. The project brings together major Indian energy developers, including Adani Green Energy, NTPC, and the Gujarat State Electricity Corporation. The park’s output will be sufficient to power about 18 million Indian homes, significantly boosting the nation’s clean energy capacity.
In addition to power generation, the project is designed to support grid stability through a planned 14 GWh battery storage system. The park is also expected to generate up to 100,000 jobs during its construction and operational phases, delivering a substantial economic boost to Gujarat. Its location on barren, uninhabited land minimizes displacement concerns while offering high solar irradiance and consistent wind speeds. Once completed by 2026, the Gujarat Hybrid Renewable Energy Park will be a symbol of India’s commitment to climate action and energy security.
2. SunZia Wind and Transmission
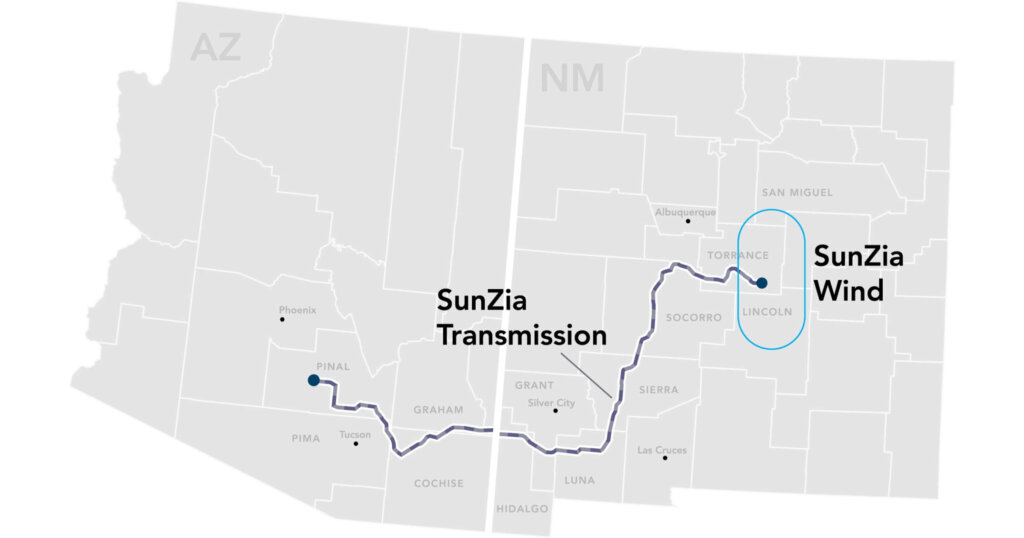
- Location: New Mexico and Arizona, United States
- Size/specs: 3.5 GW wind farm; 550-mile HVDC transmission line
- Expected timeline: Construction began in 2023; operational by 2026
SunZia Wind and Transmission is one of the largest renewable energy infrastructure projects currently under construction in the United States. Spearheaded by Pattern Energy, the project consists of a 3.5 GW wind farm located in New Mexico, paired with a 550-mile high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission line that runs through Arizona to deliver power to western markets.
The project spans two states and crosses federal, tribal, and private lands, making it one of the most complex transmission corridors permitted in decades. Its wind farm component will include more than 900 turbines, primarily manufactured by GE and Vestas, and is expected to generate enough electricity to power approximately three million homes. The HVDC line is engineered to minimize transmission losses over long distances, maximizing the value of the renewable energy generated.
With a total investment estimated at $11 billion, SunZia is a cornerstone of the energy transition in the American Southwest. It enables the large-scale integration of clean power into energy-hungry markets like Arizona and California, where demand is high and fossil fuel plants are being phased out. The renewable energy project is expected to be completed in 2026.
3. Western Green Energy Hub

- Location: Dundas Shire, Western Australia
- Size/specs: 70 GW (wind and solar) over 15,000 km²
- Expected timeline: Final investment decision by 2028
The Western Green Energy Hub is an ambitious renewable energy proposal aiming to harness 70 gigawatts of wind and solar across 15,000 square kilometers in Western Australia’s Dundas Shire. The site was chosen for its high solar irradiance, strong wind resources, and proximity to international shipping lanes. The project is a joint venture between InterContinental Energy, CWP Global, and Mirning Green Energy Limited. This collaboration has set a precedent for Indigenous inclusion in large-scale energy developments, with the Mirning community holding an equity stake in the project.
At full scale, the project is expected to produce up to 3.5 million tonnes of green hydrogen or 20 million tonnes of green ammonia annually. The green hydrogen will primarily serve export markets in Asia, helping countries like Japan and South Korea meet aggressive emissions targets. The scale of this build requires extensive transmission, desalination, and port infrastructure, all of which are being studied in the lead-up to the final investment decision, expected by 2028. Beyond its energy output, the Western Green Energy Hub has become a global case study of how massive renewable energy zones can coexist with ecological preservation and cultural heritage.
4. Mammoth Solar

- Location: Indiana, United States
- Size/specs: 1.6 GW solar PV across 13,000 acres
- Expected timeline: Phase 1 operational in July 2024; full completion by 2025
Mammoth Solar is poised to become the largest solar farm in the United States, marking a major milestone for utility-scale solar development in the Midwest. The project is being led by Doral Renewables, a U.S.-based subsidiary of Israel’s Doral Group, and covers 13,000 acres of land in Starke and Pulaski counties, Indiana. Phase 1, delivering 480 megawatts of solar power, went online in July 2024 and feeds electricity into the Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO) grid.
With the full buildout planned for 1.6 gigawatts, Mammoth Solar is a long-term commitment to clean energy in a region historically reliant on coal and natural gas. Its location was strategically selected for its flat terrain, transmission access, and supportive local governments.
When completed, the project will generate enough electricity to power roughly 250,000 homes, significantly reducing carbon emissions and easing pressure on aging grid infrastructure.
5. Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind (CVOW)

- Location: 27 miles off the coast of Virginia Beach, United States
- Size/specs: 2.6 GW from 176 Siemens Gamesa turbines across 112,800 acres of water
- Expected timeline: Construction began in November 2023; operational by 2026
Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind (CVOW) is an offshore wind energy initiative currently underway in the United States. Developed by Dominion Energy, the project includes 176 Siemens Gamesa turbines, each rated at 14.7 megawatts, spread across 112,800 acres of federally leased waters. Once operational, CVOW will generate enough electricity to power over 660,000 homes in Virginia, a significant contribution to both regional energy needs and broader decarbonization goals.
The project is located 27 miles off the coast of Virginia Beach to take advantage of strong, steady Atlantic winds while minimizing visual and environmental impact. CVOW’s estimated $10.7 billion budget includes investments in local infrastructure, ports, and supply chains that could reshape the region’s economic outlook. Dominion Energy is also positioning the project as a foundation for building a long-term domestic manufacturing base for offshore wind components.
This includes potential blade, tower, and nacelle production facilities, as well as new training programs for turbine technicians and offshore construction workers. Virginia aims to transition to 100% carbon-free electricity by 2050, and CVOW is central to that plan.
6. Dogger Bank Wind Farm

- Location: 125–290 km off the northeast coast of England
- Size/specs: 3.6 GW across three phases
- Expected timeline: Phases A and B will be operational in 2025; Phase C in 2026
Dogger Bank Wind Farm is poised to become the largest offshore wind development in the world, stretching across three phases: Dogger Bank A, B, and C. Each phase will deliver 1.2 GW of capacity, collectively capable of producing enough energy to power six million UK homes. The project is being developed by SSE Renewables, Equinor, and Vårgrønn, and it’s located in the shallow waters of the North Sea, where consistent wind speeds boost turbine performance.
A major design feature is the use of GE’s Haliade-X 13 MW and 14 MW turbines. These turbines allow for greater energy capture per unit, reducing the cost of electricity and minimizing the environmental footprint by requiring fewer foundations.
The construction effort also supports a sizable workforce, with roughly 3,000 jobs expected to be created across manufacturing, marine engineering, and ongoing operations. The project’s scale has drawn global attention as a model for high-output offshore wind, particularly as countries seek scalable solutions to reduce reliance on fossil fuels. With Phases A and B expected to go live in 2025, Dogger Bank is on track to reshape offshore wind benchmarks worldwide.
7. Empire Wind

- Location: Off the coast of Long Island, New York, United States
- Size/specs: 2.1 GW offshore wind farm over 80,000 acres of water
- Expected timeline: Construction began in 2023; operational date pending
Empire Wind is one of the largest offshore wind projects planned in the U.S., developed by Norwegian energy company Equinor. The site spans over 80,000 acres in federal waters and will feature turbines standing up to 873 feet tall. Once completed, it’s expected to deliver clean electricity to more than half a million homes in New York City, helping the state meet its target of 70% renewable energy by 2030. However, construction has hit roadblocks, with regulatory delays and permitting issues leading to financial strain and growing concerns about the timeline. Equinor reported a $300 million impairment charge in 2024, signaling a reevaluation of the project’s pace and budget.
Even with setbacks, Empire Wind remains central to New York’s offshore wind ambitions. The project is tied to major infrastructure upgrades, including onshore substations and transmission links planned for the South Brooklyn Marine Terminal. If realized, Empire Wind could bring thousands of union jobs during construction and long-term maintenance, supporting local economies in Brooklyn and Staten Island.
8. Green Volt Offshore Wind Farm

- Location: North Sea, United Kingdom
- Size/specs: 560 MW floating offshore wind farm
- Expected timeline: Final investment decision expected in 2025; operational by 2028/29
Green Volt is expected to become Europe’s first full-scale commercial floating offshore wind farm. It is being developed by Flotation Energy and Vårgrønn, a joint venture between Italian energy giant Eni and Norwegian investment firm HitecVision. The project will include up to 35 floating turbines anchored in the North Sea. It is designed to supply electricity to oil and gas platforms, reducing their carbon footprint while also feeding power back into the UK national grid.
The project has also made headlines due to the potential involvement of Chinese turbine manufacturer Mingyang Smart Energy. Concerns have been raised in UK political circles regarding national security and foreign ownership of critical infrastructure, prompting a review by the Department for Business and Trade. While no final decisions have been made, the outcome of this review could impact procurement and construction timelines.
9. ReNew Integrated Green Energy Project

- Location: Bethapalli, Anantapur district, Andhra Pradesh, India
- Size/specs: 1.8 GW solar, 1 GW wind, 2 GW battery storage
- Expected timeline: Phase 1 foundation laid in May 2025
ReNew’s Integrated Green Energy Project in Andhra Pradesh is set to be the largest hybrid renewable facility in India. The first phase includes 587 MW of solar, 250 MW of wind, and 415 MW of battery storage, combining a total investment of ₹22,000 crore (around USD 2.65 billion). It’s designed to supply uninterrupted, clean power by using battery storage to smooth out supply when generation dips. This scale of energy storage is still uncommon in India, which adds to the project’s significance. ReNew Power is leading the development and expects the project to serve as a model for future hybrid energy hubs.
The site in Bethapalli was chosen for its strong solar potential and open land, located in a district with limited industrial development. The project is part of a larger effort to attract investment to Andhra Pradesh through customized incentives and fast-tracked permitting. With a combined 4.8 GW of capacity, this site will play a role in helping India reach its 2030 clean energy targets. It’s expected to power millions of homes and support nearby industries with consistent, renewable energy.
10. Neom Green Hydrogen Project

- Location: Oxagon, Neom, Saudi Arabia
- Size/specs: 4 GW of solar and wind powering 600 tonnes/day green hydrogen plant
- Expected timeline: Operational by 2026
Saudi Arabia’s Neom Green Hydrogen Project is one of the world’s most ambitious renewable energy projects, aiming to position the kingdom as a global leader in clean hydrogen production. The facility is being developed by a joint venture of Air Products, ACWA Power, and Neom and is part of Saudi Arabia’s broader $500 billion Neom smart city initiative. The hydrogen plant is designed to produce 600 tonnes of green hydrogen per day using 4 GW of solar and wind power.
Solar and wind installations in the surrounding desert and coastal areas will feed renewable power to electrolyzers on site, producing hydrogen that is then converted into ammonia for easier transport and export. The ammonia will be shipped globally, primarily to markets in Europe and Asia looking to decarbonize the industrial and transportation sectors. The project reflects Saudi Arabia’s strategy to diversify its economy away from fossil fuels and establish itself in the fast-emerging hydrogen export market.
11. H2Med Hydrogen Pipeline
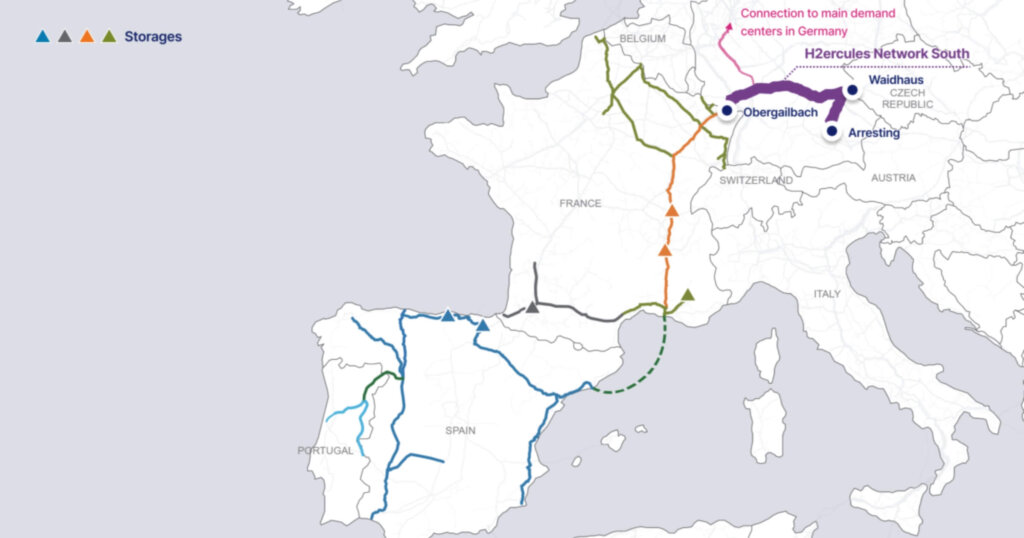
- Location: Spain, Portugal, France, and Germany (EU)
- Size/specs: 3 hydrogen pipelines totaling 3,300 km, transporting up to 2 million tonnes of hydrogen per year
- Expected timeline: First operational route by 2030; construction underway in 2025
Backed by the European Commission and part of the EU’s REPowerEU initiative, H2Med is a transnational hydrogen pipeline system linking Portugal and Spain to France and eventually Germany. The system will carry green hydrogen produced from wind and solar sources in the Iberian Peninsula to industrial hubs across central Europe. Construction of the initial segments began in early 2025 with environmental studies, permitting, and early-stage groundwork.
The scale of this renewable energy project is immense. Once complete, H2Med will span 3,300 km and deliver up to 10% of Europe’s projected hydrogen demand by 2030. The project includes three segments. BarMar (Barcelona to Marseille), CelZa (Celorico da Beira in Portugal to Zamora in Spain), and an extension toward Germany.
The initiative is led by energy companies such as Enagás (Spain), REN (Portugal), and GRTgaz (France).
Largest upcoming renewable energy megaprojects
1. Sun Cable’s Australia-Asia PowerLink (AAPowerLink), Australia
This $30+ billion project aims to be one of the largest solar energy and battery storage systems in the world. It will transmit electricity from the Northern Territory to Singapore via a 4,200 km subsea cable. Construction is slated to begin in 2025, with the goal of delivering power by the early 2030s.
2. Hollandse Kust West Wind Farm, Netherlands
A next-generation offshore wind farm featuring smart grid integration, ecological innovation, and AI-based predictive maintenance. Scheduled for construction starting in 2025, the project will contribute roughly 1.4 GW to the Dutch grid.
Are renewable energy projects growing in 2025?
Renewable energy construction is experiencing significant growth in 2025, driven by record-breaking investments, supportive policies, and technological advancements. Here is a breakdown of the factors driving the growth:
Investment trends
Global investment in the energy transition reached a record $2.1 trillion in 2024, marking an 11% increase from the previous year. This surge encompasses various sectors, including renewables, energy storage, and electrified transport. In the United States, financing for energy technologies, such as renewable energy and power grid investments, totaled $338 billion in 2024, up from $303 billion in 2023.
Policy support
The Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) has been instrumental in bolstering the U.S. renewable energy sector. Since its enactment, the IRA has spurred $145 billion in clean energy infrastructure and $73 billion in manufacturing investments. These incentives have led to quadrupling solar manufacturing capacity in the U.S. to 31 gigawatts since the Act’s passage.
Sector-specific growth
Offshore wind energy is gaining momentum, with projects like the Coastal Virginia Offshore Wind (CVOW) aiming to add 2.6 GW of capacity. Additionally, advancements in floating wind turbines are enabling deployment in deeper waters, expanding the potential for offshore wind farms.
Emerging trends in renewable energy construction
Looking ahead, several emerging trends are set to shape the renewable energy landscape:
- Advanced Energy Storage: Solid-state batteries are making significant strides, offering safer and more efficient energy storage solutions that are crucial for grid stabilization and renewable integration.
- Floating Offshore Wind Turbines: These innovations allow for wind farm deployment in deeper waters, expanding the geographical scope of offshore wind energy projects.
- Modular renewable microgrids: Compact, scalable energy systems are being deployed in remote and disaster-prone regions. These microgrids are seeing growth in Alaska, rural Africa, and Southeast Asia as decentralized power becomes a resilience strategy.
- Agri-solar integration: Agrivoltaics are on the rise in Europe, Japan, and parts of the U.S.—combining solar panel installations with agricultural production to optimize land use and reduce environmental conflict.
- AI for predictive maintenance and efficiency: Large renewable energy operators are rolling out AI-based platforms for monitoring wind turbine stress, optimizing solar output, and managing battery life cycles more accurately.
If you’re interested in the technologies and projects shaping global infrastructure, check out some of our other article deep dives:
- Data center construction projects underway in 2025
- 10 of the largest airport megaprojects underway in the U.S.
- 8 innovations for alternative energy
- These new technologies are modernizing the U.S. energy industry
Want the latest in construction and energy innovation sent straight to your inbox? Subscribe to the Under the Hard Hat newsletter and stay ahead of the curve.


